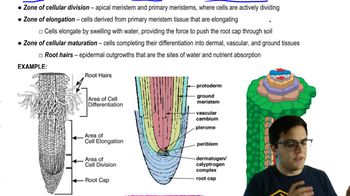
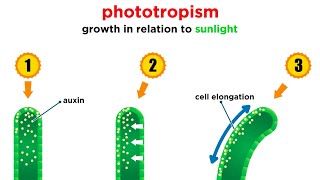
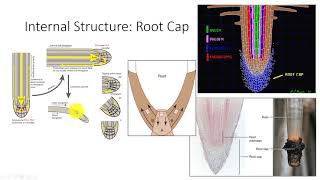
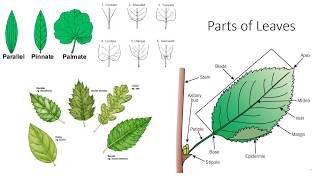
33. Plant Anatomy
Growth
33. Plant Anatomy
Growth
Additional 13 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 16 of 16 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceIf you wanted to plant a flowering plant in your yard that would bloom every spring, which of the following should you choose?1055views
- Multiple ChoiceA region of dividing cells in a plant is called a __________.1324views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich example below is the site of primary growth that results in the plant's increasing in height?1122views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following is a lateral meristem?1567views