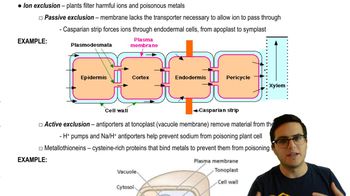
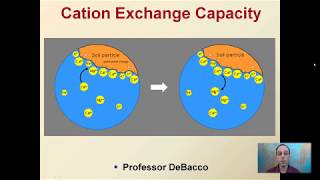
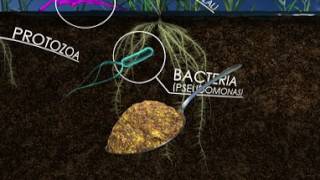
35. Soil
Soil and Nutrients
35. Soil
Soil and Nutrients
Additional 13 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 16 of 16 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceHow might roots react when they encounter a region of the soil that is low in nitrates?984views
- Multiple ChoiceThe American Dust Bowl of the 1930s resulted from __________.917views
- Multiple ChoiceSoil can easily become deficient in __________ because these ions are negatively charged and do not stick to negatively charged soil particles.1294views
- Multiple ChoiceThe particles in soil are important because they __________.1340views