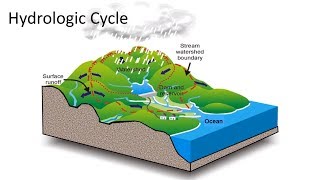
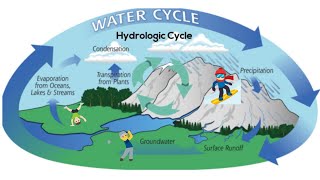
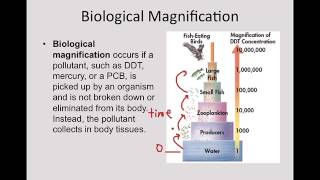
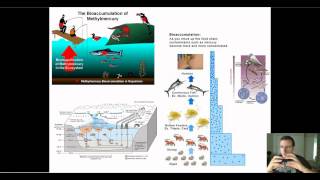
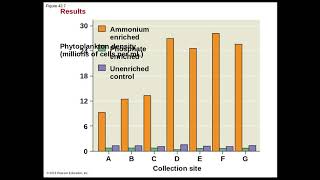
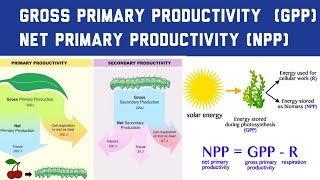
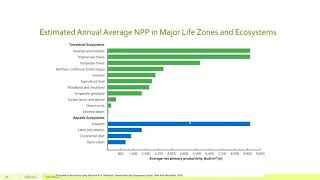
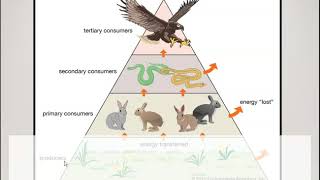
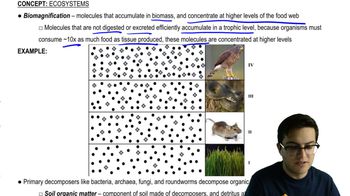
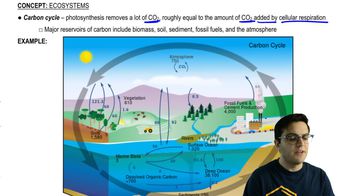
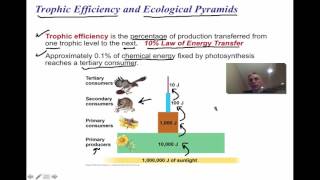
52. Ecosystems
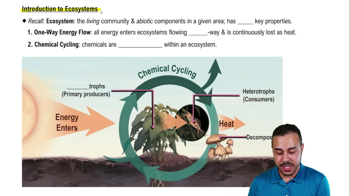
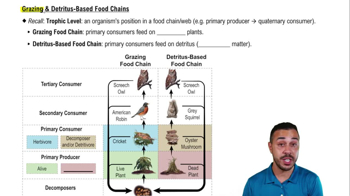
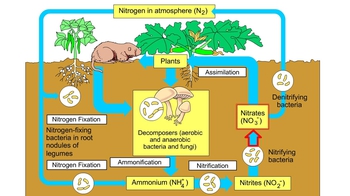
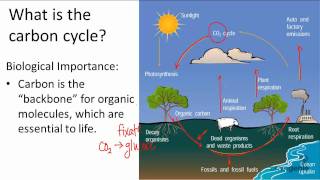
Introduction to Ecosystems
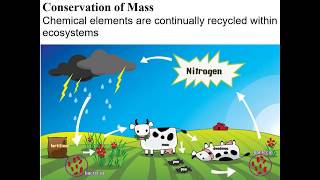
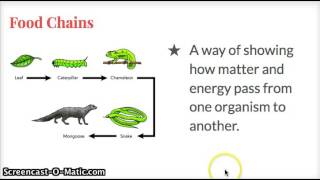
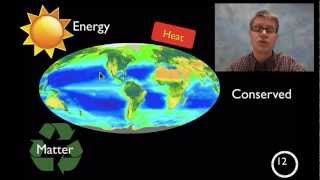
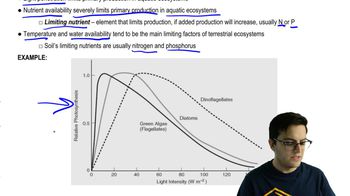
52. Ecosystems
Introduction to Ecosystems
Additional 57 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 60 of 60 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following is an ecosystem?1685views
- Multiple ChoiceThe biggest difference between the flow of energy and the flow of chemical nutrients in an ecosystem is that __________.1770views
- Multiple ChoiceIn an ecosystem, what will eventually happen to all incoming energy?1983views
- Multiple ChoiceThe main decomposers in an ecosystem are __________.1682views