8. Respiration
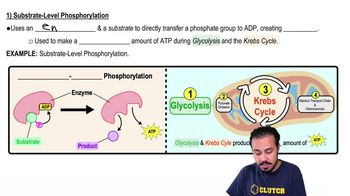
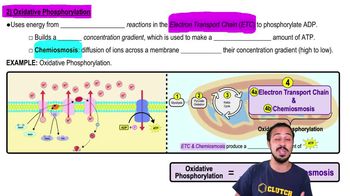
Types of Phosphorylation
8. Respiration
Types of Phosphorylation
Additional 3 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 6 of 6 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Substrate-level phosphorylation is utilized to create ATP in which steps of aerobic cellular respiration?
6589views65rank2comments - Multiple Choice
Which type of phosphorylation synthesizes ATP using an enzyme that transfers a phosphate group to ADP?
5361views53rank - Multiple Choice
The largest amount of ATP made by cellular respiration is created by the process of ______________, in the _____________ steps of aerobic cellular respiration.
5483views75rank - Multiple ChoiceMost of the ATP produced in cellular respiration comes from which of the following processes?3006views