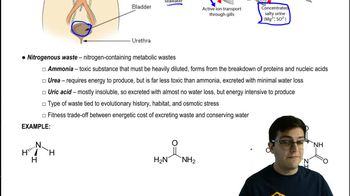
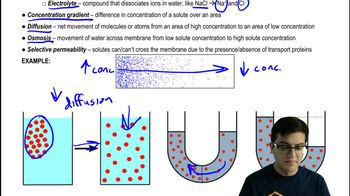
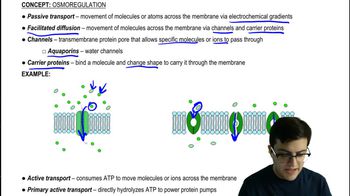
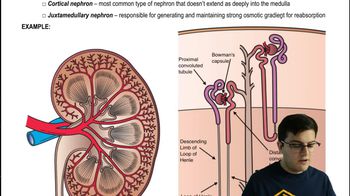
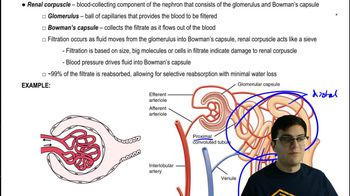
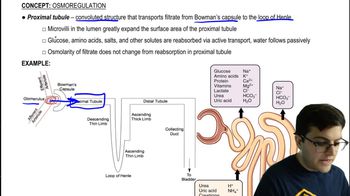
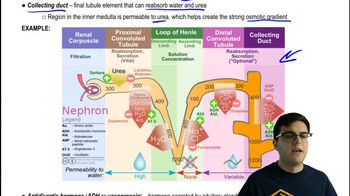
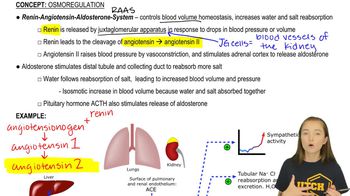
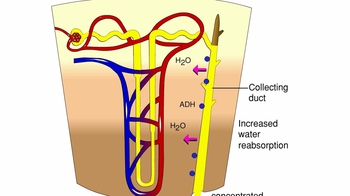
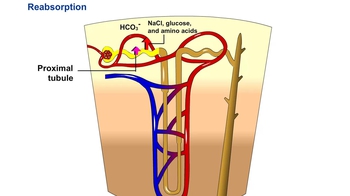
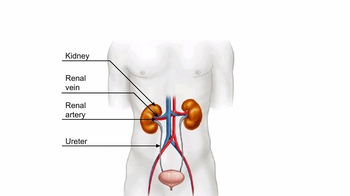
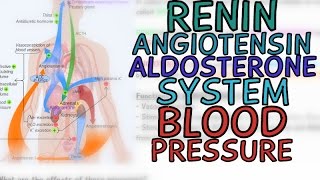
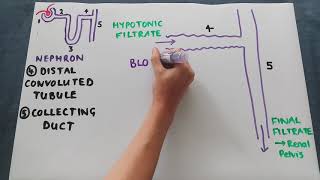
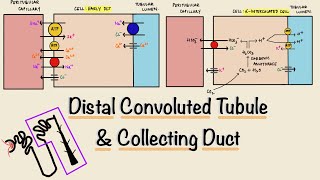
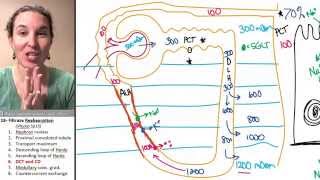
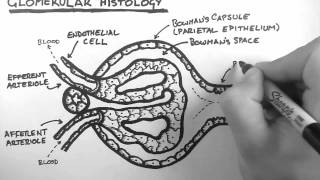
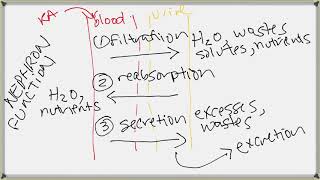
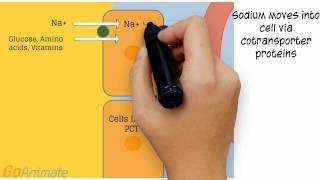
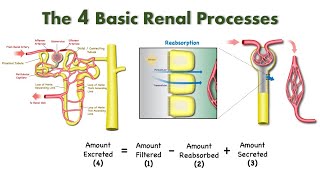
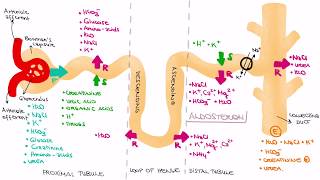
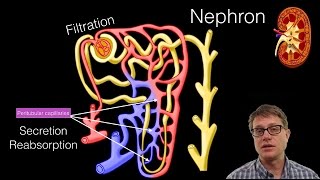
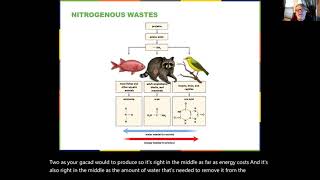
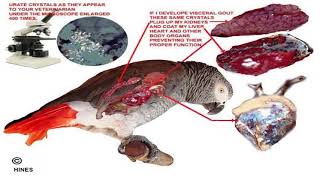
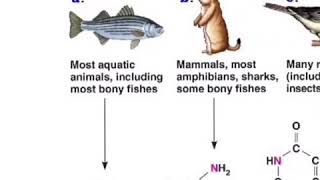
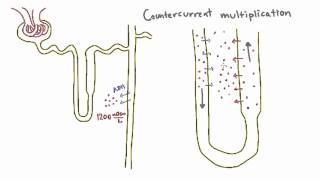
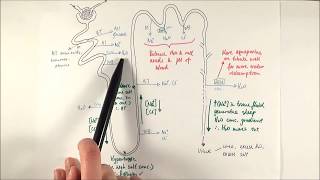
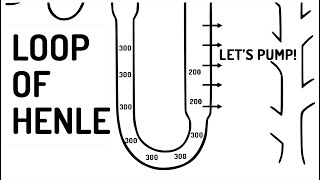
42. Osmoregulation and Excretion
Osmoregulation and Excretion
42. Osmoregulation and Excretion
Osmoregulation and Excretion
Showing 10 of 10 videos
Additional 53 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 56 of 56 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceAn albatross spending its life hovering over the ocean provides an extreme example of __________, the process by which animals control solute concentrations and balance water gain and loss.1363views
- Multiple ChoiceOsmoconformers are animals that __________.1468views
- Multiple ChoiceIn a marine environment, animals that are isoosmotic relative to their environment __________.1489views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich type of organism would have the least chance of long-term survival in the given environment?1101views