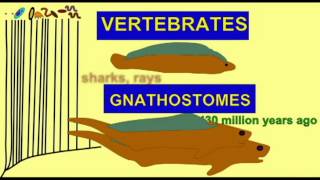
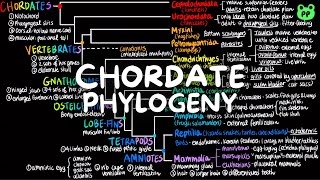
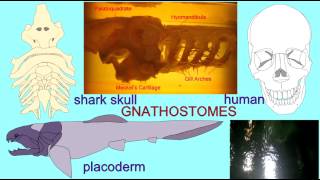
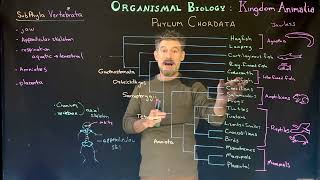
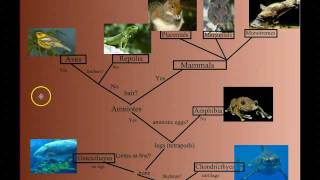
32. Vertebrates
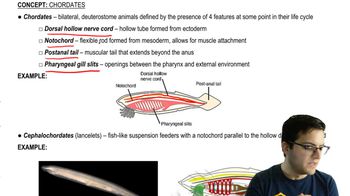
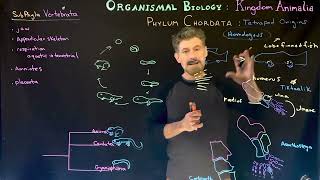
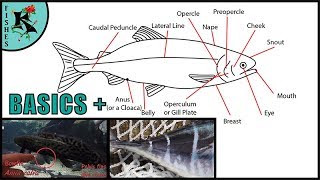
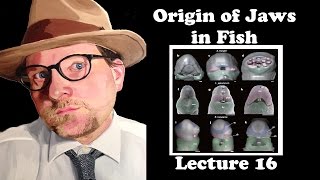
Chordates
32. Vertebrates
Chordates
Showing 6 of 6 videos
Additional 16 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 19 of 19 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceIf an animal has segments, bilateral symmetry, pharyngeal clefts, a post-anal tail, and deuterostomic development, it must be a member of the __________.1143views
- Multiple ChoiceA __________ is a chordate but not a vertebrate.1387views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following chordate characteristics contributes most to the formation of your ears?1242views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following chordate characteristics contributes most to suspension-feeding devices in many invertebrate chordates?1181views