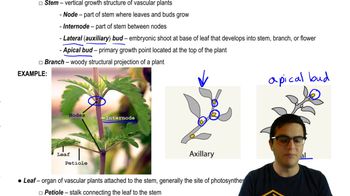
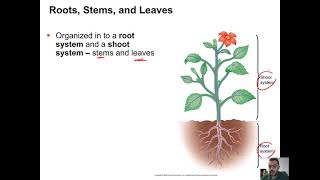
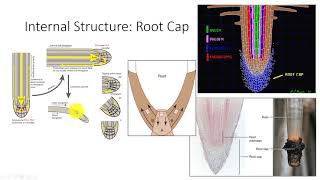
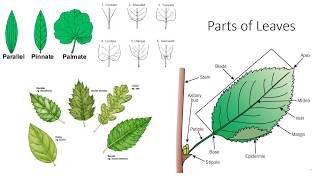
33. Plant Anatomy
Roots and Shoots
33. Plant Anatomy
Roots and Shoots
Additional 9 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 12 of 12 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceIn the hierarchy of biological organization, what is the shoot?1886views
- Multiple ChoiceA root hair is __________.1646views
- Multiple ChoiceLeaves occur at intervals along the plant stem. What is the region where a leaf is attached to the stem?1335views
- Multiple ChoiceLeaves consist of __________.1345views