6. The Membrane
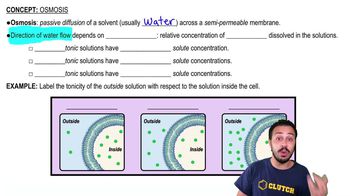
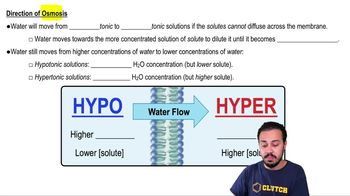
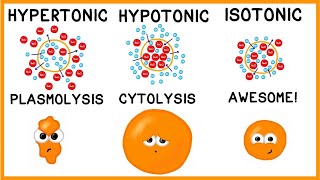
Osmosis
6. The Membrane
Osmosis
Additional 5 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 8 of 8 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Osmosis is best defined as the movement of:
7648views72rank - Multiple Choice
Which direction would you expect water to move across the cell membrane?
5605views69rank - Multiple Choice
Plants become turgid when placed in this type of solution:
4725views56rank - Multiple Choice
What would you expect to happen to the cell under the following conditions?
4929views66rank2comments