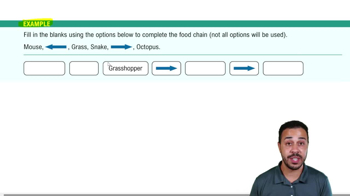
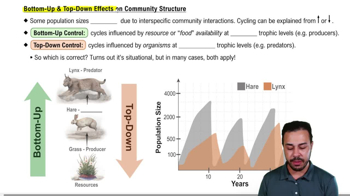
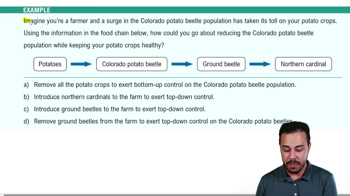
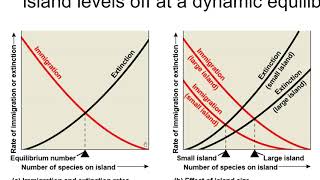
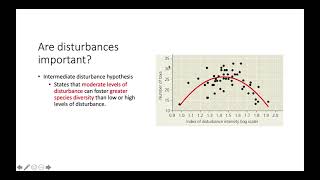
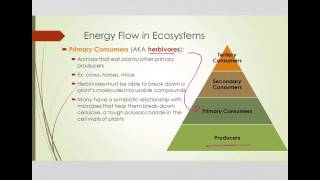
51. Community Ecology
Community Structure
51. Community Ecology
Community Structure
Showing 8 of 8 videos
Additional 33 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 36 of 36 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceA field contains 950 kg of plant material. How many kilograms of tertiary consumers could be supported?1574views
- Multiple ChoiceWhy does succession of communities occur?1677views
- Multiple ChoiceWhat is the current view of biological communities?1790views1rank
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following statements correctly describes conditions on a glacier moraine during the reign of pioneer species?1109views