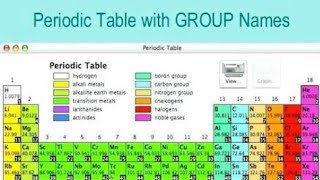
2. Atoms & Elements
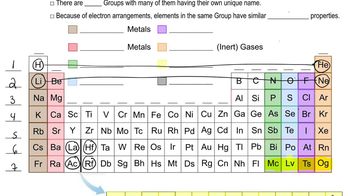
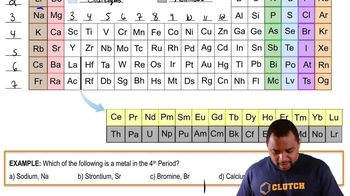
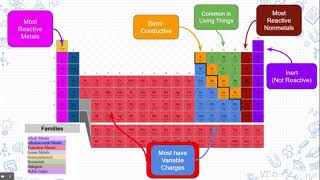
Periodic Table: Group Names
2. Atoms & Elements
Periodic Table: Group Names
Additional 6 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 9 of 9 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a metalloid that is also a chalcogen?
3008views26rank - Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following elements has properties most similar to Mg?952views
- Open Question
Which element has chemical properties that are most similar to the chemical properties of sulfur, S?
923views - Open Question
What property do all of the Group 18 elements have that makes them stand out from other elements?
794views - Open Question
This is a group of elements with few valence electrons that conducts heat and electricity.
633views - Open Question
How can you use the periodic table of elements to help you find information about specific elements?
811views - Multiple ChoiceWhat characteristic do elements in the same group of the periodic table share?354views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following statements about groups in the periodic table is not true?424views