7. Gases
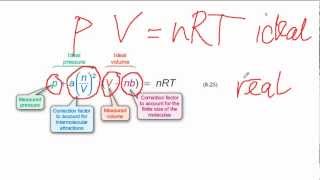
Van der Waals Equation
7. Gases
Van der Waals Equation
Additional 4 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 7 of 7 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which gaseous compound is expected to have the largest value for the Van der Waals constant b?
1040views3rank - Open QuestionWhich statement(s) concerning the van der waals constants a and b is true?623views
- Open Question
A real gas differs from an ideal gas because the molecules of real gas have
637views1comments - Multiple ChoiceVan der Waals interactions may result under which of the following conditions?238views
- Multiple ChoiceIn the van der Waals equation, which term accounts for the intermolecular attractions between gas molecules?75views
- Multiple ChoiceIn the van der Waals equation, for which property of real gases does the factor 'b' provide a correction compared to ideal gases?68views