8. Thermochemistry
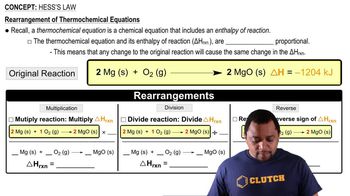
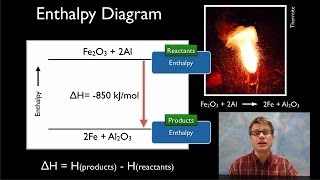
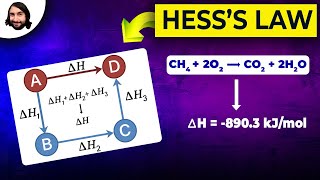
Hess's Law
8. Thermochemistry
Hess's Law
Additional 6 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 9 of 9 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Calculate the∆Hrxnfor the following thermochemical equation:
When given the following:
3348views1rank - Multiple Choice
Calculate the∆Hrxnfor
Given the following set of reactions:
3406views16rank1comments - Multiple Choice
Calculate the∆Hrxn for
Given the following reactions:
4796views9rank - Multiple ChoiceFind ΔHrxn for the following reaction:
N2 + 2 O2 → 2 NO2
Based on the following data.
2 NO → N2 + O2 ΔH = −180 kJ
2 NO + O2 → 2 NO2 ΔH = −112 kJ1016views - Open Question
Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction 4B(s) + 3O2(g) → 2B2O3(s)
1014views - Open QuestionConsider the combustion of liquid methanol ch3oh(l)1122views
- Open Question
Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction 4B(s) + 3O2(g) → 2B2O3(s).
683views - Open Question
Consider the reaction H2O(l) → H2O(g), ΔH =44.0 kJ what will ΔH be for the reaction if it is reversed?
918views