8. Thermochemistry
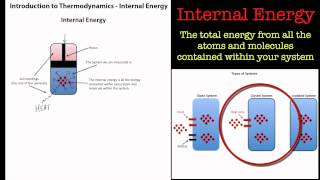
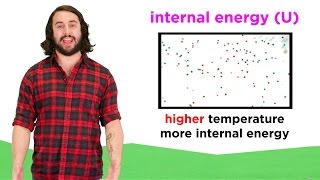
Internal Energy
8. Thermochemistry
Internal Energy
Additional 5 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 8 of 8 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
An unknown gas expands in a container increasing the volume from 4.3 L to 8.2 L at a constant pressure of 931 mmHg. Calculate the internal energy of the system if the system absorbs 2.3 kJ of energy.
1729views13rank4comments - Multiple Choice
A gas reaction is allowed to take place in a canister while submerged in water at a temperature of 25oC. The gas expands and does P-V work on the surroundings equal to 385 J. At the same time, the temperature of the water decreases to 20oC as the energy in the gas reaction reaches 364 J. What is the change in energy of the system?
1583views10rank4comments - Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following represents a state function?1077views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following processes must always result in a net increase in internal energy of the system?969views
- Open QuestionClassify the following by the sign of δe for the system.915views
- Open QuestionWhich statement is true of the internal energy of a system and its surroundings during an energy exchange with a negative δusys ?800views
- Open Question
Does a change in energy always indicate that a chemical reaction has taken place?
716views