8. Thermochemistry
Enthalpy of Formation
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
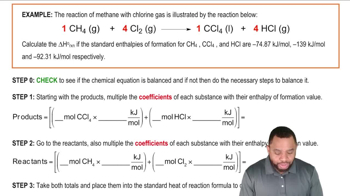
The oxidation of ammonia is illustrated by the following equation:
4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 4 NO (g) + 6 H2O (g)
Calculate the enthalpy of reaction,ΔHRxn, based on the given standard heats of formation.
3714views3rank - Multiple Choice
Consider the following equation:
2 ClF3(g) + 2 NH3(g) → 1 N2(g) + 6 HF (g) + 6 Cl2(g)ΔHrxn = –1196 kJ
Determine the standard enthalpy of formation for chlorine trifluoride, ClF3.
4269views4rank3comments - Multiple ChoiceFind ΔHrxn for the following reaction:
N2 + 2 O2 → 2 NO2
Based on the following data.
2 NO → N2 + O2 ΔH = −180 kJ
2 NO + O2 → 2 NO2 ΔH = −112 kJ1066views - Multiple ChoiceIn which of the following is ΔH°rxn = ΔH°f at 1 atm and 298 K?861views
- Open Question
Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g) given the following reactions and enthalpies of formation: 12N2(g) + O2(g) → NO2(g), δH∘a=33.2 kJ 12N2(g) + 12O2(g) → NO(g), δH∘b=90.2 kJ
1408views - Open Question
What is the isobaric heat of combustion for ethane, C2H6(g), in kJ per mole of ethane at 298.15 k?
681views - Open Question
How much energy is required to decompose 765 g of PCl3
696views - Open Question
What is the heat of combustion of ethane, C2H6, in kilojoules per mole of ethane? Enthalpy of formation values can be found in this list of thermodynamic properties.
625views