14. Solutions
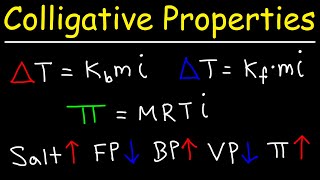
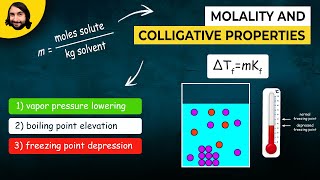
Freezing Point Depression
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
How many moles of ethylene glycol, C2H6O2, must be added to 1,000 g of water to form a solution that has a freezing point of –10ºC?
1669views7rank1comments - Multiple Choice
An ethylene glycol solution contains 28.3 g of ethylene glycol, C2H6O2 in 97.2 mL of water. Calculate the freezing point of the solution. The density of water 1.00 g/mL.
3695views6rank - Multiple Choice
When 825 g of an unknown is dissolved in 3.45 L of water, the freezing point of the solution is decreased by 2.89°C. Assuming that the unknown compound is a non-electrolyte, calculate its molar mass.
1397views3rank - Multiple ChoiceCalculate the mass of KCl used to prepare a solution in 3.00 L of water with a freezing point of –1.20 °C. Assume that the density of water = 1.00 g/mL.851views
- Open Question
Determine the freezing point depression of a solution that contains 30.7 g glycerin (C3H8O3, molar mass = 92.09 g/mol) in 376 ml of water. Some possibly useful constants for water are kf = 1.86°C/m and kb = 0.512°C/m.
1106views - Open Question
Determine the freezing point of a solution that contains 78.8 g of naphthalene (C10H8, molar mass = 128.16 g/mol) dissolved in 722 ml of benzene (d = 0.877 g/ml). pure benzene has a melting point of 5.50 °C and a freezing point depression constant of 4.90 °C/m.
974views - Open Question
What mass of glucose (C6H12O6) should be dissolved in 12.0 kg of water to obtain a solution with a freezing point of -5.8∘C?
1202views - Open Question
Calculate the freezing point of a solution containing 1.25g of benzene in 100g of chloroform
782views