13. Liquids, Solids & Intermolecular Forces
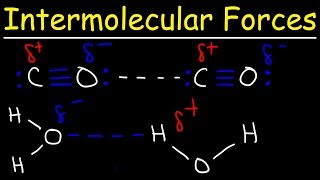
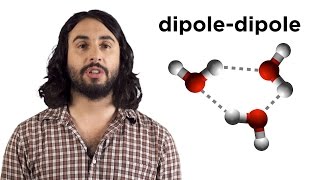
Intermolecular Forces
13. Liquids, Solids & Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular Forces
Additional 7 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 10 of 10 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
The dominant forces between molecules (intermolecular forces) are ____ in origin.
2531views22rank - Multiple Choice
Intermolecular forces are:
2148views37rank - Multiple Choice
Which of the following intermolecular forces are found in ALL molecules?
2539views8rank - Multiple Choice
Which of these molecules exhibit the highest number of different intermolecular forces?
1601views10rank4comments - Open Question
Given the distribution of charges shown in this water molecule, why is it called polar?
829views - Open Question
Which statement best helps explain the formation of the hydrogen bond represented in the figure?
847views - Open Question
What intermolecular forces are present between two molecules of HI?
1294views - Open Question
Rank the intermolecular forces in the order of increasing strength.
1176views