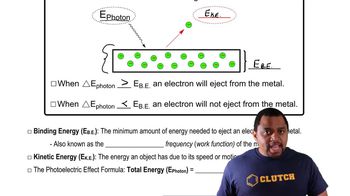
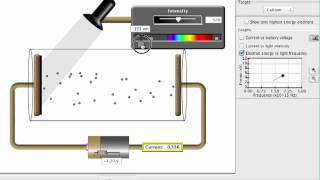
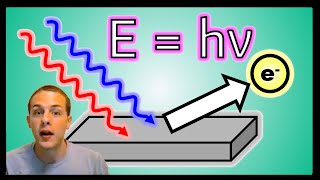
9. Quantum Mechanics
Photoelectric Effect
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
A metal with a threshold frequency of 2.15 x 1015 s-1 emits an electron with a velocity of 7.03 x 106 m/s when radiation of 4.88 x 1015 s-1 strikes the metal's surface. Calculate the mass of the electron.
3911views10comments - Multiple Choice
An ultraviolet photon with a wavelength of 320 nm strikes a metal surface. The emitted electron has a kinetic energy of 3.0 x 10-2 eV. What is the binding energy of the electron in kJ/mol? 1 electron volt (eV) = 1.602 x 10-19 J.
2216views5rank2comments - Multiple ChoiceWhich best describes the photoelectric effect?1080views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following is true about the photoelectric effect?1125views
- Open Question
What is the threshold frequency ν0 of cesium?
766views - Open Question
What is the threshold frequency for sodium metal if a photon with frequency 6.66 × 1014 s−1 ejects an electron with 7.74 × 10−20 J kinetic energy? Will the photoelectric effect be observed if sodium is exposed to orange light?
784views - Open Question
A ray of red light has a wavelength of about 7.00×10−7 m. Will exposure to red light cause electrons to be emitted from cesium?
572views - Open QuestionWhat is the threshold frequency ν0 of cesium1991views