10. Periodic Properties of the Elements
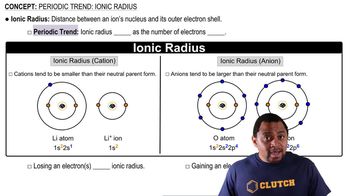
Periodic Trend: Ionic Radius
10. Periodic Properties of the Elements
Periodic Trend: Ionic Radius
Additional 4 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 7 of 7 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Arrange the following atoms and/or ions in the order of increasing size:Br –, Kr, Rb+, Sr2+.
2715views9rank - Multiple Choice
For an isoelectronic series of ions, the ion that is the smallest is always
2976views11rank - Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following atoms or ions is the largest?677views
- Open Question
When electrons are added to the outermost shell of a carbon atom, it forms
729views - Open Question
Which ion has the largest radius Br- Cl- F- I-
749views - Open QuestionWhich ion has the largest radius910views
- Open QuestionThe following ions contain the same number of electrons. rank them in order of decreasing ionic radii.706views
- Multiple Choice
Arrange the following isoelectronic series in order of decreasing radius: F–, O2– , Mg2+, Na+.
454views