11. Bonding & Molecular Structure
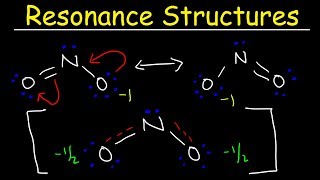
Resonance Structures
11. Bonding & Molecular Structure
Resonance Structures
Additional 4 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 7 of 7 videos
Practice this topic
- Open Question
Draw all possible resonance structures for the chlorate ion, ClO3–?
3366views10rank6comments - Multiple Choice
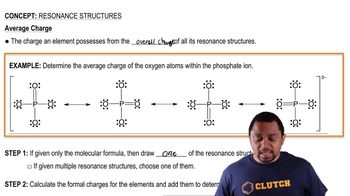
Determine the average charge of the oxygen atoms within the chlorite ion, ClO2–.
1362views6rank3comments - Multiple Choice
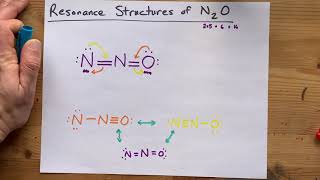
Determine which of the following drawings would be the best structure for the N2O molecule.
1382views4rank1comments - Multiple Choice
Which of the following phosphate, PO43- Lewis structures is the best, most valid resonance structure?
9287views3rank2comments - Open Question
Draw all the resonance structures for the following ionic compound:RbIO2
1745views9rank7comments - Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following substances exhibits resonance?1073views
- Open Question
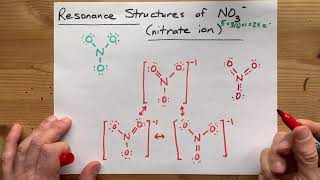
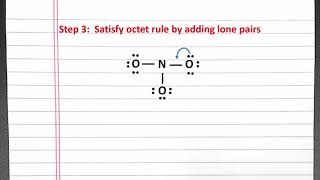
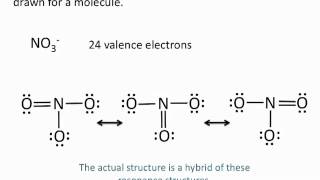
Draw the Lewis structures for three resonance forms of the nitrate ion, NO3−. Include electron lone pairs, and any formal charges.
1008views1comments - Open Question
The formate ion, HCO2−, is formed when formic acid dissolves in water. A number of possible resonance structures for this ion are shown. Which of these structures are valid and which are invalid?
1205views