Textbook Question
Differentiate among pili, fimbriae, and cilia, using sketches and descriptive labels.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: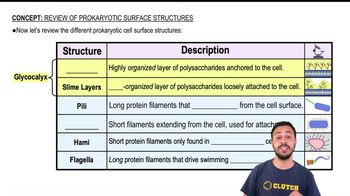


 3:52m
3:52mMaster Review of Prokaryotic Surface Structures with a bite sized video explanation from Jason
Start learning