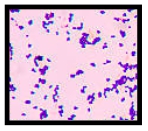
The Gram stain is a crucial technique in microbiology used to differentiate bacterial species based on their cell wall composition. This differential staining method categorizes bacteria into two primary groups: Gram-positive and Gram-negative. The Gram staining process consists of four distinct steps, each contributing to the final visualization of the bacteria.
In the first step, a crystal violet dye is applied to the bacterial sample, staining all cells purple, regardless of their classification. Initially, both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria appear unstained, but after this step, they both take on the purple hue of the crystal violet.
The second step involves treating the sample with an iodine solution, which acts as a mordant. This mordant enhances the retention of the crystal violet dye in Gram-positive cells, ensuring that they hold onto the dye more effectively. At this stage, all cells remain purple, but the Gram-positive cells have a stronger affinity for the dye.
In the third step, a decolorizer, typically alcohol or acetone, is applied. This step is critical as it differentiates the two groups: Gram-positive cells retain the purple color, while Gram-negative cells lose the crystal violet dye and become colorless. This step highlights the structural differences in the cell walls, with Gram-positive bacteria having a thicker peptidoglycan layer that retains the dye.
The final step involves applying a counterstain, Safranin, to the now colorless Gram-negative cells. This counterstain imparts a pinkish color to the Gram-negative bacteria, allowing for clear visual differentiation. By the end of the Gram staining process, Gram-positive cells remain purple, while Gram-negative cells appear pink.
Ultimately, the Gram stain provides a simple yet effective method for identifying and categorizing bacteria, facilitating further study and understanding of microbial characteristics. This foundational technique is essential for microbiologists and plays a significant role in clinical diagnostics and research.