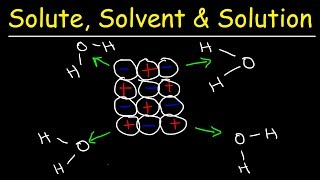
14. Solutions
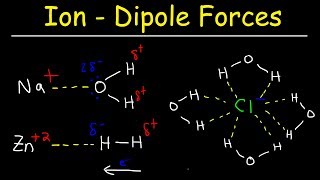
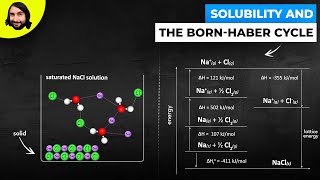
Solutions: Solubility and Intermolecular Forces
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Indicate the most important type of intermolecular attraction responsible for solvation in the following solution:
Methanol, CH3OH, dissolved in ethanol, CH3CH2OH
2342views19rank - Multiple Choice
Which of the following solutes will most readily dissolve in H2O?
2639views29rank2comments - Multiple Choice
Two pure chemical substance are likely to mix and form a solution if:
1884views10rank2comments - Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is/are true?
I. The hydrocarbon methane (CH4) will dissolve completely in acetone (CH3COCH3).
II. Ammonia (NH3) will form a heterogeneous mixture with carbon tetrachloride (CCl4).
III. Pentane (C5H12) will form a homogeneous mixture with carbon tetrabromide (CBr4).
IV. Methanethiol (CH3SH) is miscible in fluoromethane (CH3F).
2155views21rank1comments - Open Question
Which lists mixtures, in order, from the smallest particles to the largest particles?
669views - Open Question
Which interactions and processes contribute to the dissolution of ionic compounds in water?
812views - Open Question
Which statement accurately describes part of the dissolving process of a polar solute in water?
693views - Open QuestionChoose the pair of substances that are most likely to form a homogeneous solution.1099views