8. Thermochemistry
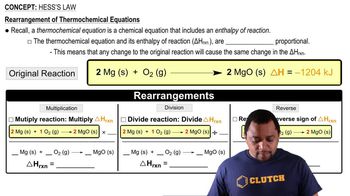
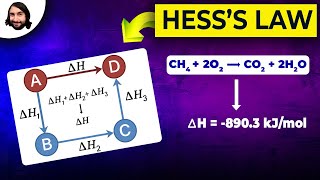
Hess's Law
Problem 95
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionHess's law can be used to calculate reaction enthalpies for hypothetical processes that can't be carried out in the labo- ratory. Set up a Hess's law cycle that will let you calculate ∆H° for the conversion of methane to ethylene: 2 CH4(g) → C2H4(g) + 2 H2(g) You can use the following information: 2 C2H6(g) + 7 O2(g) → 4 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(l) ∆H° = -3120.8 kJ CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l) ∆H° = -890.3 kJ C2H4(g) + H2(g) → C2H6(g) ∆H° = -136.3 kJ H2O(l) ∆H°f = -285.8 kJ/mol
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
879
views
Was this helpful?
Related Videos
Related Practice
Showing 1 of 13 videos