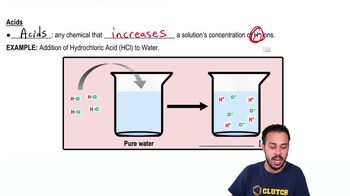
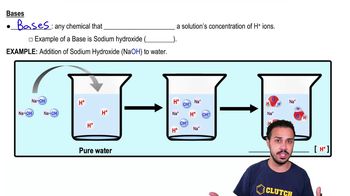
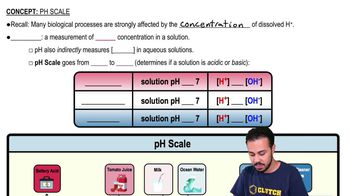
Classify each of the molecules on the left as an acid, base, or salt. The dissociation products of the molecules are shown to help you.
H2SO4 → 2H+ + SO42⁻
a. Acid
b. Base
c. Salt
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: