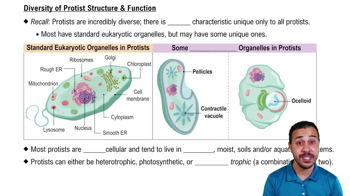
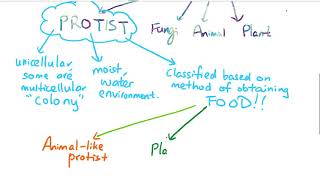
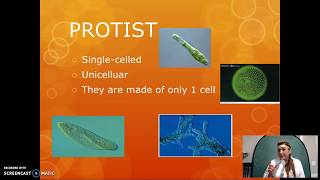
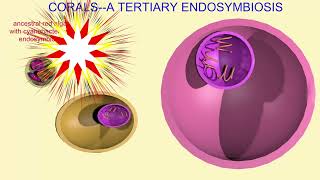
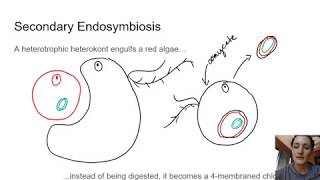
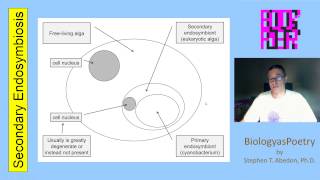
27. Protists
Introduction to Protists
27. Protists
Introduction to Protists
Additional 15 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 18 of 18 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceWhat percentage of the world's photosynthesis is carried out by protists?1127views
- Multiple ChoiceHypermastigotes are important endosymbionts that live in the guts of __________.1113views
- Multiple ChoiceThe placement of all protists in one kingdom caused dissatisfaction among taxonomists mainly because __________.901views
- Multiple Choice
Complete the sentence: All protists ____________.
835views12rank