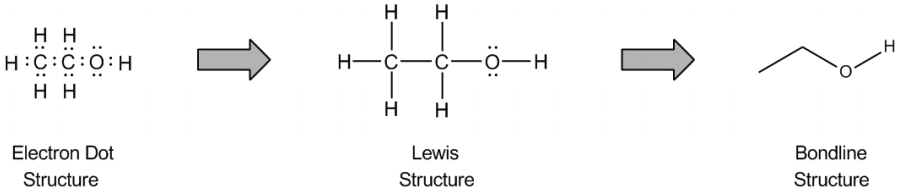
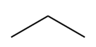
The bond line method is a simplified way to represent organic molecules, primarily focusing on carbon structures while adhering to the octet rule. Understanding the octet rule is crucial, as it allows for the efficient conversion of detailed molecular drawings into more manageable bond line structures. In these structures, carbon atoms are implied at every vertex or corner of the zigzag pattern, eliminating the need to write out each carbon explicitly. This approach streamlines the representation of complex organic compounds.
In addition to carbon, hydrogen atoms are also implied in bond line structures. The number of hydrogen atoms attached to a carbon can be deduced based on the octet rule. For instance, if a carbon atom forms two bonds with other carbons, it must have two hydrogen atoms to complete its octet of eight electrons. This mental subtraction helps in visualizing the implied hydrogens without cluttering the drawing.
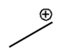
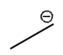
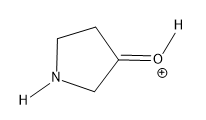
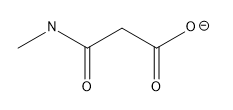
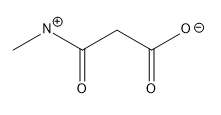
Lone pairs of electrons are similarly implied in bond line structures. A heteroatom, defined as any atom that is not carbon (such as nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine), is assumed to have enough lone pairs to satisfy its octet unless specified otherwise, particularly in the presence of formal charges. Formal charges are essential in these structures, as they indicate when an atom does not meet its bonding preferences. Instead of drawing lone pairs, formal charges are used to clarify the bonding situation.
It is important to note that all hydrogen atoms bonded to heteroatoms must be explicitly drawn. This requirement prevents confusion regarding the presence of hydrogens and lone pairs on heteroatoms, ensuring clarity in the representation of the molecule. By following these conventions, the bond line method provides a clear and efficient way to depict organic molecules while adhering to the principles of the octet rule.