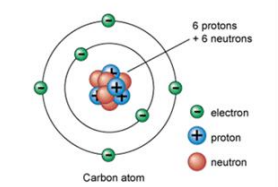
Atoms are the fundamental units of matter, and when combined, they form molecules. At the core of an atom lies the nucleus, which contains the majority of the atom's mass, composed of protons and neutrons. Although the nucleus is very small compared to the entire atom, it plays a crucial role in defining the atom's properties. Surrounding the nucleus are electrons, which occupy various energy levels or orbits.
The atomic number of an atom is determined by the number of protons it contains. This number is unique to each element, meaning that no two elements can have the same atomic number. In addition to the atomic number, we also consider the mass number, which is the total count of protons and neutrons within the nucleus. The mass number can be calculated using the formula:
Mass Number = Number of Protons + Number of Neutrons
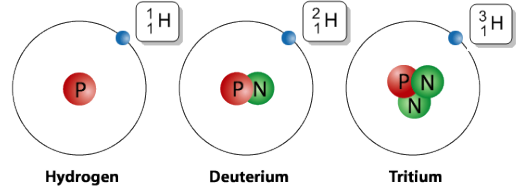
Isotopes are variations of a particular element that share the same number of protons (and thus the same atomic number) but differ in the number of neutrons. This difference in neutrons results in varying mass numbers among isotopes of the same element. Understanding isotopes is essential for grasping concepts in nuclear chemistry and applications such as radiometric dating and medical imaging.