Textbook Question
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following:
b.
1051
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: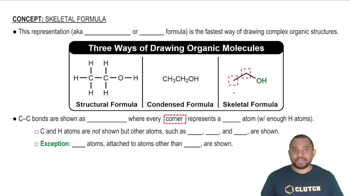

 :49m
:49mMaster Alkyl Halides Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning