Gibbs free energy, denoted as ΔG, is a crucial concept in thermodynamics that quantifies the energy change associated with a chemical or physical process capable of performing work. The sign of ΔG is instrumental in determining the spontaneity of a reaction. When ΔG is less than 0 (negative), the reaction is considered spontaneous, indicating that it can occur without external input. Conversely, if ΔG is greater than 0 (positive), the reaction is non-spontaneous, meaning it requires energy to proceed. In cases where ΔG equals 0, the system is at equilibrium, signifying a state where the forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate, and there is no net change. Understanding the implications of ΔG is essential for predicting the behavior of chemical reactions and their feasibility in various conditions.
- 1. Matter and Measurements4h 29m
- What is Chemistry?7m
- The Scientific Method9m
- Classification of Matter16m
- States of Matter8m
- Physical & Chemical Changes19m
- Chemical Properties8m
- Physical Properties5m
- Intensive vs. Extensive Properties13m
- Temperature (Simplified)9m
- Scientific Notation13m
- SI Units (Simplified)5m
- Metric Prefixes24m
- Significant Figures (Simplified)11m
- Significant Figures: Precision in Measurements7m
- Significant Figures: In Calculations19m
- Conversion Factors (Simplified)15m
- Dimensional Analysis22m
- Density12m
- Specific Gravity9m
- Density of Geometric Objects19m
- Density of Non-Geometric Objects8m
- 2. Atoms and the Periodic Table5h 22m
- The Atom (Simplified)9m
- Subatomic Particles (Simplified)12m
- Isotopes17m
- Ions (Simplified)22m
- Atomic Mass (Simplified)18m
- Atomic Mass (Conceptual)12m
- Periodic Table: Element Symbols6m
- Periodic Table: Classifications11m
- Periodic Table: Group Names8m
- Periodic Table: Representative Elements & Transition Metals7m
- Periodic Table: Elemental Forms (Simplified)6m
- Periodic Table: Phases (Simplified)8m
- Law of Definite Proportions9m
- Atomic Theory9m
- Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment9m
- Wavelength and Frequency (Simplified)5m
- Electromagnetic Spectrum (Simplified)11m
- Bohr Model (Simplified)9m
- Emission Spectrum (Simplified)3m
- Electronic Structure4m
- Electronic Structure: Shells5m
- Electronic Structure: Subshells4m
- Electronic Structure: Orbitals11m
- Electronic Structure: Electron Spin3m
- Electronic Structure: Number of Electrons4m
- The Electron Configuration (Simplified)22m
- Electron Arrangements5m
- The Electron Configuration: Condensed4m
- The Electron Configuration: Exceptions (Simplified)12m
- Ions and the Octet Rule9m
- Ions and the Octet Rule (Simplified)8m
- Valence Electrons of Elements (Simplified)5m
- Lewis Dot Symbols (Simplified)7m
- Periodic Trend: Metallic Character4m
- Periodic Trend: Atomic Radius (Simplified)7m
- 3. Ionic Compounds2h 18m
- Periodic Table: Main Group Element Charges12m
- Periodic Table: Transition Metal Charges5m
- Periodic Trend: Ionic Radius (Simplified)5m
- Periodic Trend: Ranking Ionic Radii8m
- Periodic Trend: Ionization Energy (Simplified)9m
- Periodic Trend: Electron Affinity (Simplified)8m
- Ionic Bonding6m
- Naming Monoatomic Cations6m
- Naming Monoatomic Anions5m
- Polyatomic Ions25m
- Naming Ionic Compounds11m
- Writing Formula Units of Ionic Compounds7m
- Naming Ionic Hydrates6m
- Naming Acids18m
- 4. Molecular Compounds2h 18m
- Covalent Bonds6m
- Naming Binary Molecular Compounds6m
- Molecular Models4m
- Bonding Preferences6m
- Lewis Dot Structures: Neutral Compounds (Simplified)8m
- Multiple Bonds4m
- Multiple Bonds (Simplified)6m
- Lewis Dot Structures: Multiple Bonds10m
- Lewis Dot Structures: Ions (Simplified)8m
- Lewis Dot Structures: Exceptions (Simplified)12m
- Resonance Structures (Simplified)5m
- Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (Simplified)4m
- Electron Geometry (Simplified)8m
- Molecular Geometry (Simplified)11m
- Bond Angles (Simplified)11m
- Dipole Moment (Simplified)15m
- Molecular Polarity (Simplified)7m
- 5. Classification & Balancing of Chemical Reactions3h 17m
- Chemical Reaction: Chemical Change5m
- Law of Conservation of Mass5m
- Balancing Chemical Equations (Simplified)13m
- Solubility Rules16m
- Molecular Equations18m
- Types of Chemical Reactions12m
- Complete Ionic Equations18m
- Calculate Oxidation Numbers15m
- Redox Reactions17m
- Spontaneous Redox Reactions8m
- Balancing Redox Reactions: Acidic Solutions17m
- Balancing Redox Reactions: Basic Solutions17m
- Balancing Redox Reactions (Simplified)13m
- Galvanic Cell (Simplified)16m
- 6. Chemical Reactions & Quantities2h 34m
- 7. Energy, Rate and Equilibrium3h 40m
- Nature of Energy6m
- First Law of Thermodynamics7m
- Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions7m
- Bond Energy14m
- Thermochemical Equations12m
- Heat Capacity19m
- Thermal Equilibrium (Simplified)8m
- Hess's Law23m
- Rate of Reaction11m
- Energy Diagrams12m
- Chemical Equilibrium7m
- The Equilibrium Constant14m
- Le Chatelier's Principle20m
- Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)17m
- Spontaneous vs Nonspontaneous Reactions7m
- Entropy (Simplified)9m
- Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified)18m
- 8. Gases, Liquids and Solids3h 27m
- Pressure Units6m
- Kinetic Molecular Theory14m
- The Ideal Gas Law18m
- The Ideal Gas Law Derivations13m
- The Ideal Gas Law Applications6m
- Chemistry Gas Laws17m
- Chemistry Gas Laws: Combined Gas Law12m
- Standard Temperature and Pressure14m
- Dalton's Law: Partial Pressure (Simplified)13m
- Gas Stoichiometry18m
- Intermolecular Forces (Simplified)19m
- Intermolecular Forces and Physical Properties11m
- Atomic, Ionic and Molecular Solids10m
- Heating and Cooling Curves30m
- 9. Solutions4h 27m
- Solutions6m
- Solubility and Intermolecular Forces17m
- Solutions: Mass Percent6m
- Percent Concentrations10m
- Molarity18m
- Osmolarity15m
- Parts per Million (ppm)13m
- Solubility: Temperature Effect8m
- Intro to Henry's Law4m
- Henry's Law Calculations12m
- Dilutions12m
- Solution Stoichiometry14m
- Electrolytes (Simplified)13m
- Equivalents11m
- Molality15m
- The Colligative Properties15m
- Boiling Point Elevation16m
- Freezing Point Depression9m
- Osmosis16m
- Osmotic Pressure10m
- Vapor Pressure Lowering (Raoult's Law)16m
- 10. Acids and Bases3h 10m
- Acid-Base Introduction11m
- Arrhenius Acid and Base6m
- Bronsted Lowry Acid and Base21m
- Acid and Base Strength17m
- Ka and Kb16m
- The pH Scale16m
- Auto-Ionization9m
- pH of Strong Acids and Bases9m
- Acid-Base Equivalents14m
- Acid-Base Reactions7m
- Gas Evolution Equations (Simplified)6m
- Ionic Salts (Simplified)11m
- Buffers11m
- Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation16m
- Strong Acid Strong Base Titrations (Simplified)13m
- 11. Nuclear Chemistry56m
- BONUS: Lab Techniques and Procedures1h 38m
- BONUS: Mathematical Operations and Functions47m
- 12. Introduction to Organic Chemistry1h 34m
- 13. Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic Compounds2h 12m
- 14. Compounds with Oxygen or Sulfur1h 6m
- 15. Aldehydes and Ketones1h 1m
- 16. Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives1h 11m
- 17. Amines39m
- 18. Amino Acids and Proteins1h 51m
- 19. Enzymes1h 37m
- 20. Carbohydrates1h 41m
- Intro to Carbohydrates4m
- Classification of Carbohydrates4m
- Fischer Projections4m
- Enantiomers vs Diastereomers7m
- D vs L Enantiomers9m
- Cyclic Hemiacetals8m
- Intro to Haworth Projections4m
- Cyclic Structures of Monosaccharides11m
- Mutarotation4m
- Reduction of Monosaccharides10m
- Oxidation of Monosaccharides7m
- Glycosidic Linkage14m
- Disaccharides7m
- Polysaccharides2m
- 21. The Generation of Biochemical Energy2h 8m
- 22. Carbohydrate Metabolism2h 22m
- 23. Lipids2h 26m
- Intro to Lipids6m
- Fatty Acids25m
- Physical Properties of Fatty Acids6m
- Waxes4m
- Triacylglycerols12m
- Triacylglycerol Reactions: Hydrogenation8m
- Triacylglycerol Reactions: Hydrolysis13m
- Triacylglycerol Reactions: Oxidation7m
- Glycerophospholipids15m
- Sphingomyelins13m
- Steroids15m
- Cell Membranes7m
- Membrane Transport10m
- 24. Lipid Metabolism1h 45m
- 25. Protein and Amino Acid Metabolism1h 37m
- 26. Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis2h 54m
- Intro to Nucleic Acids4m
- Nitrogenous Bases16m
- Nucleoside and Nucleotide Formation9m
- Naming Nucleosides and Nucleotides13m
- Phosphodiester Bond Formation7m
- Primary Structure of Nucleic Acids11m
- Base Pairing10m
- DNA Double Helix6m
- Intro to DNA Replication20m
- Steps of DNA Replication11m
- Types of RNA10m
- Overview of Protein Synthesis4m
- Transcription: mRNA Synthesis9m
- Processing of pre-mRNA5m
- The Genetic Code6m
- Introduction to Translation7m
- Translation: Protein Synthesis18m
Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified): Videos & Practice Problems
Gibbs free energy () predicts reaction spontaneity: negative values indicate spontaneous reactions, positive values non-spontaneous, and zero denotes equilibrium. Spontaneity also depends on enthalpy () and entropy (), with temperature influencing outcomes. The key formula is , where units must be consistent, typically converting entropy to kilojoules. Understanding these thermodynamic principles is essential for predicting chemical reaction behavior and equilibrium.
Gibbs Free Energy is energy change associated with a thermodynamic process that can be used to do non-mechanical work.
Gibbs Free Energy
Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified) Concept 1
Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified) Concept 1 Video Summary

Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified) Example 1
Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified) Example 1 Video Summary
In the context of reversible reactions, the Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) provides insight into the spontaneity of a reaction. When ΔG is small and positive, it indicates that the reaction is non-spontaneous in the forward direction, meaning that the reactants are favored over the products. This small positive value suggests that the system is close to equilibrium, as ΔG approaches zero at equilibrium.
In this scenario, since the forward reaction is non-spontaneous, the reverse reaction becomes spontaneous. Therefore, while the forward reaction does not proceed readily, the reverse reaction can occur with relative ease. The proximity of ΔG to zero signifies that the system is near equilibrium, where the concentrations of reactants and products are balanced, allowing for the possibility of both forward and reverse reactions to occur.
In summary, when ΔG is small and positive, the reaction is non-spontaneous in the forward direction but spontaneous in the reverse direction, and the system is near equilibrium.
Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified) Concept 2
Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified) Concept 2 Video Summary
In thermodynamics, the spontaneity of a chemical reaction can be assessed using the signs of enthalpy change (ΔH) and entropy change (ΔS). When both ΔH and ΔS are positive, the reaction is spontaneous at high temperatures. Conversely, if both ΔH and ΔS are negative, the reaction is spontaneous at low temperatures. This indicates that temperature plays a crucial role in determining spontaneity based on the signs of these thermodynamic quantities.
In scenarios where ΔH is positive and ΔS is negative, the reaction is always non-spontaneous, regardless of temperature. On the other hand, if ΔH is negative and ΔS is positive, the reaction is spontaneous. This relationship can be summarized as follows: for reactions to be spontaneous, the combination of ΔH and ΔS must align with the temperature conditions. Understanding these principles allows for predicting the feasibility of reactions under varying thermal conditions.
Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified) Example 2
Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified) Example 2 Video Summary
In the reaction between phosphorus trichloride (PCl3) and chlorine gas (Cl2) to form phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5), the enthalpy change (ΔH) is reported as -92.50 kJ at 25 degrees Celsius. This negative value indicates that the reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases heat rather than absorbing it. Consequently, the statement claiming this is an endothermic reaction is incorrect.
When considering the equilibrium constant (K), which is defined as the ratio of products to reactants, an increase in temperature affects the position of equilibrium. Since the reaction produces one product from two reactants, the entropy change (ΔS) is negative due to the decrease in disorder. As temperature increases, the spontaneity of the reaction decreases, leading to a preference for the reactants over the products. This shift results in a decrease in the equilibrium constant (K), as the concentration of reactants increases relative to products.
To summarize the thermodynamic parameters: ΔH is negative, indicating an exothermic reaction, while ΔS is also negative, reflecting a decrease in entropy. The Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) will only be negative (indicating spontaneity) at lower temperatures, not at all temperatures. Therefore, the only accurate statement regarding this reaction is that ΔS for the reaction is negative, confirming the decrease in entropy as reactants combine to form a single product.
What are the signs of ∆H, ∆S and ∆G for the spontaneous conversion of a solid into gas?

–∆H; –∆S; +∆G
–∆H; +∆S; +∆G
–∆H; +∆S; –∆G
+∆H; +∆S; –∆G
+∆H; +∆S; +∆G
You calculate the value of ΔG for a chemical reaction and get a positive value. Which would be the most accurate way to interpret this result?
If a mixture of reactants and products is created and left to equilibrate, the equilibrium mixture will contain more reactant than product.
If a mixture of reactants and products is created, we cannot say anything about its composition at equilibrium but we can say it will reach equilibrium very rapidly.
The reaction will not occur under any circumstances.
If a mixture of reactants and products is created and left to equilibrate, the equilibrium mixture will contain more product than reactant.
Consider the combustion of butane gas and predict the signs of ΔS, ΔH and ∆G.
C4H10(g) + 13/2 O2(g) ⟶ 4 CO2(g) + 5 H2O(g)
Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified) Concept 3
Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified) Concept 3 Video Summary
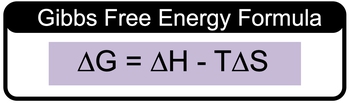
The calculation of Gibbs free energy, denoted as ΔG, is essential in thermodynamics for understanding the spontaneity of reactions. The Gibbs free energy formula is expressed as:
\( \Delta G = \Delta H - T \Delta S \)
In this equation, ΔH represents the change in enthalpy, typically provided in kilojoules (kJ), while ΔS denotes the change in entropy, usually given in joules per Kelvin (J/K). The temperature (T) is measured in Kelvin (K). It is crucial to ensure that the units for ΔH and ΔS are consistent before performing the calculation. Since ΔH is often given in kilojoules, it is standard practice to convert ΔS from joules to kilojoules by dividing by 1000, allowing for uniformity in units.
When applying this formula, remember to include the appropriate units in your calculations to maintain accuracy. The resulting value of ΔG will indicate whether a reaction is spontaneous; a negative ΔG suggests spontaneity, while a positive ΔG indicates non-spontaneity.
Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified) Example 3
Gibbs Free Energy (Simplified) Example 3 Video Summary
In thermodynamics, the spontaneity of a reaction can be determined using the Gibbs free energy change, represented by the equation:
\( \Delta G = \Delta H - T \Delta S \)
For the given reaction, the enthalpy change (\( \Delta H \)) is -111.4 kJ, and the entropy change (\( \Delta S \)) is -25 J/K. To use these values in the equation, it is essential to convert the entropy change from joules to kilojoules. This conversion involves moving the decimal point three places to the left, resulting in:
\( \Delta S = -0.025 \, \text{kJ/K} \)
Next, substituting the values into the Gibbs free energy equation at a temperature of 298 K:
\( \Delta G = -111.4 \, \text{kJ} - (298 \, \text{K} \times -0.025 \, \text{kJ/K}) \)
Calculating the second term:
\( 298 \, \text{K} \times -0.025 \, \text{kJ/K} = -7.45 \, \text{kJ} \)
Now, substituting this back into the equation gives:
\( \Delta G = -111.4 \, \text{kJ} + 7.45 \, \text{kJ} = -103.95 \, \text{kJ} \)
Since the calculated \( \Delta G \) value is less than 0, it indicates that the reaction is spontaneous at 298 K. A negative \( \Delta G \) signifies that the reaction can proceed in the forward direction without the need for external energy input. Conversely, if \( \Delta G \) were equal to 0, the system would be at equilibrium, and if \( \Delta G \) were greater than 0, the reaction would be non-spontaneous in the forward direction, favoring the reverse reaction instead.
A particular reaction has ΔG = –350 kJ and ΔS = –350 J/K at 24°C. How much heat will be released/absorbed?
For a reaction in which ΔH = 125 kJ and ΔS = 325 J/K, determine the temperature in Celsius above which the reaction is spontaneous.
Do you want more practice?
More sets



Here’s what students ask on this topic:
A negative Gibbs free energy (ΔG < 0) indicates that a chemical reaction is spontaneous. This means the reaction can proceed on its own without needing external energy input. Spontaneity implies that the process releases free energy that can be used to do work. In contrast, a positive ΔG means the reaction is non-spontaneous and requires energy input to occur, while a ΔG of zero means the system is at equilibrium, with no net change happening. Understanding the sign of ΔG helps predict whether a reaction will naturally occur under given conditions.
When ΔG is unknown, the spontaneity of a reaction can be predicted by analyzing the signs of enthalpy (ΔH) and entropy (ΔS). If both ΔH and ΔS are positive, the reaction is spontaneous at high temperatures because the entropy term (TΔS) dominates. If both are negative, the reaction is spontaneous at low temperatures since the enthalpy term (ΔH) dominates. When ΔH is positive and ΔS is negative, the reaction is always non-spontaneous. Conversely, if ΔH is negative and ΔS is positive, the reaction is always spontaneous. This approach helps determine the temperature conditions under which a reaction will proceed spontaneously.
The formula for calculating Gibbs free energy is , where ΔH is enthalpy change, T is temperature in Kelvin, and ΔS is entropy change. Typically, ΔH is given in kilojoules (kJ), and ΔS in joules per Kelvin (J/K). To ensure unit consistency, convert ΔS to kilojoules per Kelvin by dividing by 1000 before using the formula. This standardization is important for accurate calculation of ΔG, which predicts reaction spontaneity.
Unit conversion is crucial when calculating Gibbs free energy because ΔH and ΔS often have different units—ΔH in kilojoules (kJ) and ΔS in joules per Kelvin (J/K). Since the formula involves subtracting the product of temperature and entropy from enthalpy, both terms must be in the same units to avoid calculation errors. Typically, ΔS is converted from joules to kilojoules by dividing by 1000. This ensures the resulting ΔG value is accurate and meaningful for predicting reaction spontaneity.
When Gibbs free energy (ΔG) equals zero, the system is at equilibrium. This means the forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate, and there is no net change in the concentrations of reactants and products. At this point, the reaction is neither spontaneous nor non-spontaneous. Understanding this condition is important because it defines the balance point where the reaction can shift in either direction depending on changes in conditions such as temperature or pressure.