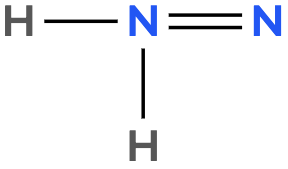
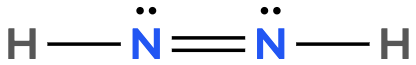
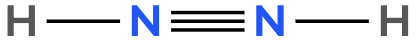Atoms often form multiple bonds when their valence electrons are insufficient to satisfy the octet rule, which states that atoms ideally seek to have eight electrons in their outer shell, similar to the electron configuration of noble gases. For instance, consider nitrogen, which can form either a single bond or a triple bond with another nitrogen atom. In the case of a single bond, a total of 10 valence electrons are utilized: each single bond consists of 2 electrons, leading to a count of 2, 4, 6, 8, and finally 10. However, this configuration leaves both nitrogen atoms with an incomplete octet, as each nitrogen only has 6 electrons surrounding it (2, 4, 6). To resolve this issue, forming a triple bond is more effective. In this arrangement, the total remains at 10 valence electrons, but now each nitrogen atom achieves a complete octet with 8 electrons (2, 4, 6, 8).
It is crucial to remember that multiple bonds, such as double or triple bonds, may be necessary to fulfill the octet rule for certain atoms. However, hydrogen is an exception; it adheres to the duet rule, desiring only 2 electrons in its outer shell to achieve a stable configuration akin to helium.