Textbook Question
What is the structural relationship between a thiol and an alcohol?
1812
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
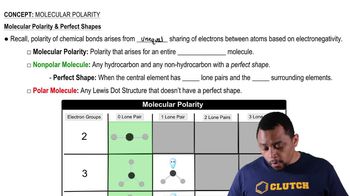


What is the structural relationship between a thiol and an alcohol?
Oxidation of a dithiol such as 2,5-hexanedithiol forms a six-membered ring containing a disulfide group as part of the ring. Draw the structure of this cyclic disulfide (Hint: Draw the starting compound in line structure format first).
The boiling point of propanol is 97 °C ,much higher than that of either ethanethiol (37 °C) or chloroethane (13 °C) , even though all three compounds have similar MWs. Explain.
Define the following terms:
b. Achiral
Define the following terms:
c. Chiral carbon
Identify the chiral center(s) in each of the following molecules:
a. 2-Methyl-3-pentanol