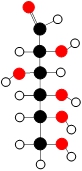
Molecular models are a valuable tool for visualizing chemical bonds between elements, utilizing color-coded balls to represent different elements from the periodic table. Each color corresponds to a specific element, aiding in the understanding of molecular structures and interactions.
For instance, a white ball symbolizes hydrogen, while a black ball denotes carbon. The sky blue ball represents nitrogen, and the red ball indicates oxygen. Additionally, a grayish off-white ball signifies fluorine, a navy blue ball stands for phosphorus, a lime green ball is used for sulfur, and finally, a forest green ball represents chlorine.
Understanding these color codes is essential for interpreting molecular models and grasping the relationships between different elements in chemical compounds. This visual representation not only enhances comprehension but also facilitates the study of molecular geometry and bonding patterns.