Solubility, often referred to as concentration or molarity, is a key concept in chemistry that describes how much solute can be dissolved in a solvent. Molarity is specifically defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution, providing a quantitative measure of solubility. When a solid solute is added to a solvent, it dissociates into ions, which then disperse throughout the solvent. However, there is a limit to how much solute can be dissolved, known as the saturation point.
A solution is considered saturated when it contains the maximum amount of dissolved solute at a given temperature and pressure. For example, if a bucket of water can dissolve 100 grams of a solute, adding 102 grams will result in 100 grams dissolving while the remaining 2 grams will remain undissolved at the bottom. In contrast, a solution is unsaturated if it contains less solute than the maximum capacity. If 90 grams of solute are added to the same bucket, all 90 grams will dissolve, leaving room for an additional 10 grams.
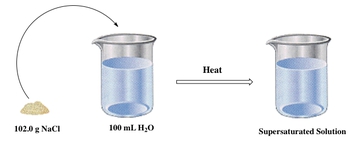
Furthermore, a supersaturated solution occurs when more solute is dissolved than the equilibrium concentration allows, which can be achieved by applying heat. For instance, if the bucket can normally dissolve 100 grams but is heated to dissolve 102 grams, it becomes supersaturated. However, this state is unstable; once the heat is removed, the excess solute will precipitate out, forming solid crystals at the bottom of the container.
In summary, understanding the distinctions between saturated, unsaturated, and supersaturated solutions is crucial for grasping the concept of solubility. All these terms relate back to the idea of how much solute can be dissolved in a solvent, emphasizing the importance of temperature and pressure in these processes.