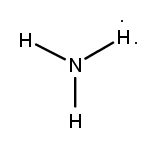
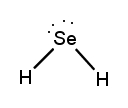
Lewis dot structures are essential tools in chemistry that visually represent the valence electrons of elements and how they form covalent bonds. These structures help illustrate the arrangement of electrons around atoms in a molecule, emphasizing the importance of valence electrons in bond formation. Atoms tend to form bonds to achieve a stable electron configuration, often resembling that of the nearest noble gas, which is characterized by a full outer electron shell.
When drawing Lewis dot structures, several key rules guide the process to ensure the most accurate representation of molecular compounds. First, it is crucial to determine the total number of valence electrons available from all the atoms involved. This total will dictate how the electrons are distributed among the atoms in the structure.
Next, the central atom is typically the least electronegative element, which is surrounded by other atoms. Single bonds are drawn between the central atom and surrounding atoms, using pairs of electrons. After establishing the initial bonds, any remaining valence electrons are placed around the outer atoms to fulfill the octet rule, which states that atoms tend to prefer having eight electrons in their valence shell.
If there are still electrons left after satisfying the outer atoms, they can be placed on the central atom. In some cases, it may be necessary to form double or triple bonds to ensure that all atoms achieve a full valence shell. This process may involve moving lone pairs of electrons from outer atoms to form additional bonds with the central atom.
Ultimately, the goal is to create the most stable structure, which minimizes formal charges across the molecule. By following these guidelines, one can effectively draw Lewis dot structures that accurately represent the bonding and electron distribution in molecular compounds.