Thermochemistry focuses on the relationship between matter and energy during chemical reactions and physical changes. Energy, defined as the capacity to perform work or generate heat, can be categorized into various forms, with particular emphasis on potential and kinetic energy in this context.
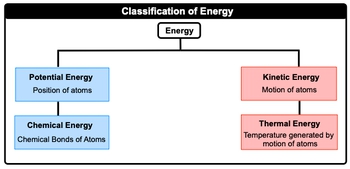
Potential energy refers to the energy associated with the position of atoms, while kinetic energy relates to the energy of motion. These two primary forms of energy can be further subdivided. Potential energy can be associated with chemical bonds, known as chemical energy, which plays a crucial role in the stability and reactivity of substances. On the other hand, kinetic energy can be linked to thermal energy, which is the energy generated by the motion of atoms and is directly related to temperature.
In summary, the key types of energy relevant to thermochemistry include:
- Potential Energy: Energy of position, including chemical energy.
- Kinetic Energy: Energy of motion, including thermal energy.
Understanding these energy forms is essential for analyzing how energy is transferred and transformed during chemical processes, laying the groundwork for deeper exploration of thermodynamic principles in subsequent studies.