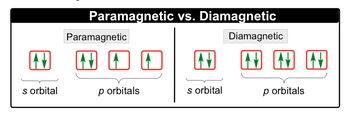
In atomic theory, understanding the behavior of electrons in orbitals is crucial, particularly when discussing the concepts of paramagnetism and diamagnetism. An orbital can accommodate a maximum of two electrons, which must have opposite spins, as dictated by the Pauli exclusion principle. This principle is fundamental in determining the magnetic properties of substances.
Paramagnetic materials contain at least one unpaired electron in their orbitals, making them responsive to external magnetic fields. For instance, in an s orbital where all electrons are paired, the substance would not exhibit paramagnetism. However, if we examine p orbitals and find an unpaired electron, the substance becomes paramagnetic. The presence of even a single unpaired electron is sufficient for a material to be classified as paramagnetic.
In contrast, diamagnetic substances have all their electrons paired within their orbitals. This means that every orbital, whether s or p, contains two electrons with opposite spins, resulting in no unpaired electrons. Consequently, diamagnetic materials are not influenced by magnetic fields.
When determining the electron configurations of elements or ions, it is essential to identify whether they are paramagnetic or diamagnetic. A paramagnetic element or ion will have at least one unpaired electron, while a diamagnetic one will have all electrons paired. This distinction is vital for predicting the magnetic behavior of various substances.