Heat or thermal energy play a pivotal role in the rate of a chemical reaction. The Arrhenius equation represents the formula that shows the dependence of the rate and rate constant k on the absolute temperature, as well as other variables such as activation energy, and the pre-exponential factor.
Rate of Reaction
Generally, as we increase the temperature of a chemical reaction, molecules will absorb this new source of thermal energy. The result is that molecules will move more quickly, striking one another more frequently and with greater force. If molecule A can hit molecule B with enough energy and the correct orientation then they will successful combine and form a new molecule AB.

Rate and Temperature
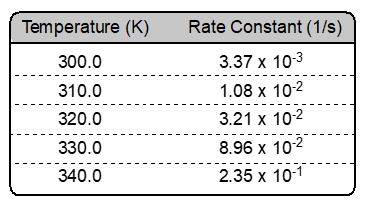
From the chart provided, as the temperature increases the rate of formation for molecule AB increases. The rule of thumb is that a rise of 10 °C will double the rate of reaction.
Arrhenius Equation
Although it was well known that increases in temperature led to increases in rate, it wasn’t until the Arrhenius Equation developed by Svante Arrhenius that this temperature-rate relationship could be accurately explained.

Arrhenius Equation
When examining the variables of the Arrhenius Equation: k is the rate constant and, Ea is the activation energy normally in J/mol or kJ/mol, T is the absolute Temperature in Kelvin, R is the universal gas constant equal to 8.314 J/mol K, and A is the pre-exponential factor, frequency factor or Arrhenius constant.

Arrhenius Equation Components
Since the pre-exponential factor is a constant based on the given chemical reaction and the universal gas constant is always the same value, the way to affect k is based on changing Ea or T. Based on the Arrhenius equation, increasing the rate constant k can be accomplished by either increasing the temperature or decreasing the activation energy, usually through the use of a catalyst.
Let’s approach a question using the Arrhenius equation.
PRACTICE: The rate constant of a reaction at 33.0 °C was measured to be 5.2 × 10−2 s−1. If the frequency factor is 1.2 × 1013 s−1, what is the activation barrier?
STEP 1: Identify the given variables.

Arrhenius Equation (Identifying Variables)
STEP 2: Convert the temperature given in Celsius to Kelvin.

Arrhenius Equation (Temperature Conversion)
STEP 3: Multiply both sides of the equation by the natural logarithm, ln.

Arrhenius Equation & Natural Log
When multiplying the Arrhenius equation by ln we obtain:

Derivation of Arrhenius Equation
Rearranging this new formula gives us the straight-line form:

Arrhenius Equation (Straight-Line Form)
STEP 4: Plug in the given values into straight-line form of the Arrhenius Equation.

Arrhenius Equation (Plugging in values)
Solving for some of the portions simplifies it to:

Arrhenius Equation (Simplification 1)
STEP 5: Subtract 30.1158 from both sides.

Arrhenius Equation (Subtracting)
This simplifies the equation to:

Arrhenius Equation (Simplification 2)
STEP 6: Multiply both sides by 8.314.

Arrhenius Equation (Multiplying by 8.314)
The equation is now:

Arrhenius Equation (Simplification 3)
STEP 6: Divide both sides by 0.003266.

Arrhenius Equation (Divide by 0.003266)
This gives the value of Ea as:

Arrhenius Equation (Isolating Ea)
Arrhenius Equation: Plot-wise approach
As we’ve shown before, the Arrhenius equation can be written in a non-exponential form or straight-line form.

Arrhenius Equation (Non-Exponential Form)
This form of the Arrhenius equation allows us to interpret our values graphically.

Ln k vs. 1/T Plot
By setting our y-axis as ln k and our x-axis as the inverse temperature we can correlate the non-exponential form of the Arrhenius equation to a straight-line.

Arrhenius Equation (y = mx + b)
By using the straight-line or non-exponential form of the Arrhenius equation we can determine either the frequency factor or the activation energy of a chemical reaction.
PRACTICE: The rate constant for a reaction was measured as a function of temperature. Based on the plot of ln k versus 1/T, what is the activation energy for the reaction?

Arrhenius Equation & Plotted Graph
STEP 1: Using the equation for the straight line from the chart provided, apply it to the non-exponential form of the Arrhenius equation.

Arrhenius Equation & Given Equation
STEP 2: Isolate the slope of the straight line and set it equal to – Ea/R.

Slope & Activation Energy
Since the universal gas constant R is equal to 8.314 J/mol K, solve for the activation energy of the chemical reaction.
STEP 3: Multiply both sides by – 8.314 to isolate the activation energy.

Slope & Isolating Ea
This gives Ea as:

Solve for Ea (J/mol)
Arrhenius Equation: 2-Point Form
The 2-point form of the Arrhenius Equation is a way mathematically calculating the changes in the rate constant k as the temperature changes. Recall that an increase in temperature causes an increase in the rate constant.

Arrhenius Equation (2-Point Form)
Depending on the placement of T1 and T2 the 2-point form of the Arrhenius equation can be written in two different ways. Algebraically either form can be used for solving.
From the 2-point form of the Arrhenius Equation: k1 and k2 are the rate constants and, Ea is the activation energy normally given in J/mol or kJ/mol, T1 and T2 are the absolute Temperatures in Kelvin, R is the universal gas constant equal to 8.314 J/mol K.
PRACTICE: The activation energy for a reaction is 37.6 kJ/mol. The rate constant for the reaction is 5.4 x 10-3 s-1 at 45 °C. Calculate the rate constant at 145 °C.
STEP 1: Identify the given variables.

Arrhenius 2 -Point Form (Identifying variables)
STEP 2: Convert the temperatures given in Celsius to Kelvin.

Arrhenius 2-Point Form (Temperature Conversions)
STEP 3: Since the universal gas constant R uses joules in its units then the activation energy Ea must be converted from kJ/mol to J/mol.

Ea (Unit Conversion)
STEP 4: Plug the given variables into the equation.

Arrhenius 2-Point Form (Plugging variables)
STEP 5: Solve the portions of the equation with values into order to simplify.

Arrhenius 2-Point Form (Simplification 1)
STEP 6: Combine the integers on the right side by multiplying them together.

Arrhenius 2-Point Form (Simplification 2)
STEP 7: Take the inverse e of the natural logarithm to both sides of the equation to further isolate k2.

Arrhenius 2-Point Form (Simplification 3)
When you take the inverse of the natural logarithm you eliminate the ln on the left side.

Arrhenius 2-Point Form (Simplification 4)
This simplifies the expression to:

Arrhenius 2-Point Form (Simplification 5)
STEP 8: Solve for the right side of the equation.

Arrhenius 2-Point Form (Simplification 6)
STEP 9: Multiply both sides by 5.4 x 10-3 s-1.

Arrhenius 2-Point Form (Multiplying by 5.4 x 10-3)
STEP 10: Isolate the value for k2.

Arrhenius 2-Point Form (Isolating k2)
The Arrhenius equations form an integral part in our study of Chemical Kinetics and give a mathematical view of how molecules successful react to form products.