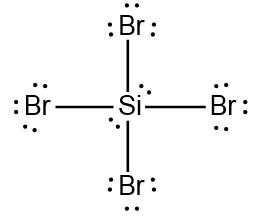
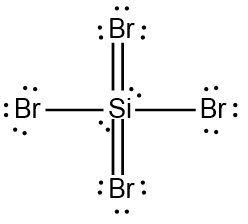
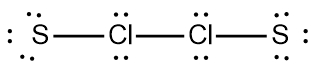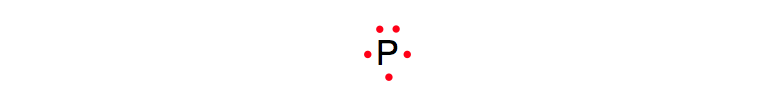A Lewis Dot structure, named after Gilbert N. Lewis, is the structural representation of a molecule that involves the use of valence electrons by the involved atoms in the creation of covalent bonds.
Lewis Dot Diagrams
Before we can start drawing Lewis electron dot structures we have to figure out how to depict the valence electrons of individual atoms.

Lewis Dot Diagrams (C, N, O, F)
From these Lewis electron-dot symbols, the element symbol represents the nucleus and inner electrons, and the surrounding dots represent the valence electrons.
Basics of Lewis Dot Diagrams
It’s easy to write the Lewis symbol for any Main-Group element and since Lewis dot structures involve non-metals we won’t have to worry about transition metals.
1) Remember that Group Number equals Valence Electron Number.
2) Place one dot at a time on the four sides starting from the top of the element and moving clockwise.
3) Keep adding dots, pairing them up until you have reached the number of total valence electrons for that element.
PRACTICE 1: Determine the electron dot diagram for the following atom:
Phosphorus (P)
STEP 1: Find the group number for the phosphorus atom and begin to fill in its valence electrons.
Since phosphorus is in Group 5A it will have 5 valence electrons.
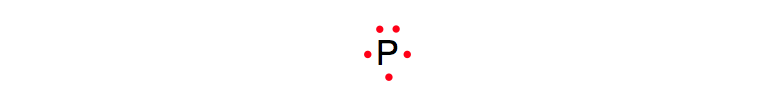
Lewis Dot Diagram (Phosphorus)
PRACTICE 2: Determine the electron dot diagram for the following ion:
Calcium ion (Ca2+)
STEP 1: When it comes to finding the electron dot diagram of an ion you should first find it for its neutral form.
Since the calcium atom is in Group 2A it will have 2 valence electrons.

Lewis Dot Diagram (Calcium)
STEP 2: Find the electron dot diagram of the cation. The 2+ charge means calcium has lost 2 valence electrons. For ions we place the element in brackets and its charge on the top right.

Lewis Dot Diagram (Calcium Ion)
PRACTICE 3: Determine the electron dot diagram for the following ion:
Oxide ion (O2–)
STEP 1: Like we did before we again find the electron dot diagram of the neutral atom.
Since the oxygen atom is in Group 6A it will have 6 valence electrons.

Lewis Dot Diagram (Oxygen)
STEP 2: Find the electron dot diagram of the anion. Again place the charge on the top right corner and brackets around the ion. The 2– charge means calcium has gained 2 valence electrons.

Lewis Dot Diagram (Oxide Ion)
How To Draw Lewis Diagrams
Lewis Dot Structures are important within chemistry because not only do they provide the structural representation of a compound, but also help to explain the reactivity, polarity and overall stability of compounds. When it comes to drawing lewis dot structures, these are the rules you should follow:
Rule 1: When drawing the structure the least electronegative element goes in the center. Recall that electronegativity increases going from left to right across a period and going from bottom to top of any group.

Periodic Trend (Electronegativity)
Hydrogen and Flourine never go in the center and they only make single bonds.
Rule 2: The number of valence electrons an element has is equal to its group number.

Group Number & Valence Electrons
Rule 3: Carbon is in Group 4A, has 4 valence electrons, and must make 4 bonds. It can accomplish this through a combination of single bonds, double bonds or triple bond.

Carbon Bonding Patterns
In rare occasions carbon can make 3 bonds when it is positively or negatively charged.

Rare Carbon Bonding Patterns
Rule 4: Nitrogen is located in Group 5A and has 5 valence electrons. Since it is 3 spaces away from being a noble gas on the periodic table then it ideally wants to make 3 bonds.

Nitrogen Bonding Patterns
Nitrogen can also create 2 or 4 bonds if necessary.

Rare Nitrogen Bonding Patterns
Nitrogen tends to create only 2 bonds when it gains an electron and 4 bonds when it loses an electron. Also the addition of an electron gives nitrogen a negative charge, while the loss of an electron gives it a positive charge.
Rule 5: Oxygen is located in Group 6A and has 6 valence electrons. Since it is 2 spaces away from being a noble gas on the periodic table then it ideally wants to make 2 bonds.

Oxygen Bonding Patterns
Oxygen can also create 1 or 3 bonds if necessary.

Rare Oxygen Bonding Patterns
Oxygen tends to create a single bond when it gains an electron and 3 bonds when it loses an electron. Also the addition of an electron gives oxygen a negative charge, while the loss of an electron gives it a positive charge.
Rule 6: When halogens, the elements in Group 7A, are surrounding elements they only make single bonds.

Halogen Bonding Patterns
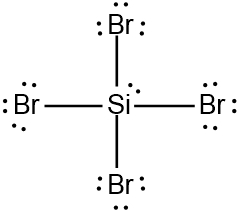
Expanded Valence Shell Theory
Based on this theory, nonmetals starting from Period 3 and lower can have more than eight electrons around them when they are the central element. They accomplish these expanded octets by using the d-orbitals within their third shell.

Expanded Octets (Nonmetals)
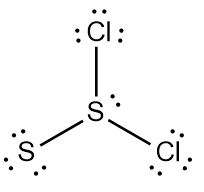
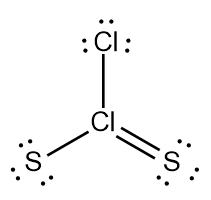
Two examples of these expanded octets can be seen with the bonding patterns of sulfur (S) and arsenic (As).

Bonding Patterns (S, As)
Formal Charge
Whenever we draw a Lewis Dot Structure we can use the formal charge formula to check to see if you drew our compound correctly.
Basics of Formal Charge
- The only allowable formal charges for an element can be either -1, 0, +1.
- If you add up all the formula charges in your compound that will equal the overall charge of the compound.
Formal Charge = Group Number – (Bonds of Element + Nonbonding electrons of Element)

Formal Charge (Thiocyanate Ion)
Lewis Structures Practice Problems
With the rules for drawing Lewis dot structures under our belts, it’s time to start drawing.
PRACTICE 1: Draw the following Lewis dot structure for CH2Cl2.
STEP 1: Determine the group number and from it the number of valence electrons for each element.

Lewis Dot Diagrams (C, H, Cl)
STEP 2: Place the least electronegative element as the central element and remember that hydrogen can never go in the center.

Lewis Dot Digram (Carbon)
STEP 3: Start adding the surrounding elements to your central element. Hydrogen can only make single bonds because it has only 1 valence electron.

Carbon & Hydrogen Bonding (CH2)
STEP 4: Halogens, like chlorine, only make single bonds when they are not a central element.

Lewis Dot Structure (CH2Cl2)
PRACTICE 2: Draw the following Lewis dot structure for C3H8.
STEP 1: Draw the Lewis dot diagrams for the elements involved.

Lewis Dot Diagrams (C, H)
STEP 2: Place the least electronegative element as the central element (hydrogen is an exception).

Central Carbon Atoms
STEP 3: Add the surrounding hydrogens to the carbon atoms. Keep in mind that carbon atoms want to make 4 bonds and hydrogen atoms want to make 1 bond.

Lewis Dot Structure (C3H8)
PRACTICE 3: Draw the following Lewis dot structure for CH3SH.
Drawing more complex Lewis dot structures can sometimes be a situation of trial and error in terms of drawing them.
STEP 1: Draw the Lewis dot diagrams for the elements involved.

Lewis Dot Diagrams (C, H, S)
STEP 2: Place the least electronegative element as the central element.

Central Element (Carbon)
STEP 3: Add the 3 hydrogen atoms around the carbon atom.

Carbon & Hydrogen Bonding (CH3)
STEP 4: Since carbon wants to make 4 bonds, attach the sulfur atom to the carbon atom by a single bond.

Carbon, Hydrogen, Sulfur Bonding (CH3S)
STEP 4: Single bond the hydrogen atom to the sulfur atom to complete the Lewis dot structure.

Lewis Dot Structure (CH3SH)
PRACTICE 4: Draw the following Lewis dot structure for CH2O.
STEP 1: Draw the Lewis dot diagrams for the elements involved.

Lewis Dot Diagrams (C, H, O)
STEP 2: Place the least electronegative element as the central element.

Lewis Dot Diagram (Central Carbon)
STEP 3: Add the 2 hydrogen atoms around the carbon atom.

Carbon & Hydrogen Bonding (CH2)
STEP 4: Since carbon wants to make 4 bonds, it would have to form a double bond with the oxygen atom.

Lewis Dot Structure (CH2O)