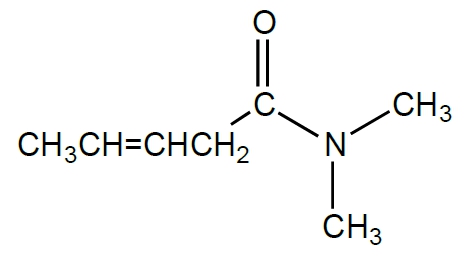
The functional group of a molecule is crucial as it determines the compound's reactivity and characteristics. Understanding how to identify different functional groups is essential in organic chemistry, starting with hydrocarbons, which are compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Hydrocarbons can be categorized based on the types of bonds between carbon atoms. The simplest form is the alkane, characterized by carbon atoms connected by single bonds. The general formula for alkanes is CnH2n+2, where n represents the number of carbon atoms. As long as the carbon atoms are single bonded to each other and to hydrogen atoms, the compound is classified as an alkane.
Next, we have alkenes, which feature at least one double bond between carbon atoms. The general formula for alkenes is CnH2n. The presence of a double bond introduces different reactivity compared to alkanes.
Moving on, alkynes are identified by having at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. The general formula for alkynes is CnH2n-2. This triple bond significantly alters the chemical properties and reactivity of the compound.
Lastly, we encounter the benzene ring, also known as an aromatic ring. This structure consists of a cyclic arrangement of carbon atoms with alternating double bonds, which contributes to its unique stability and reactivity. The benzene ring is a fundamental structure in organic chemistry, often serving as a building block for more complex molecules.
In summary, recognizing these functional groups—alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and benzene rings—is foundational for further studies in organic chemistry, as they dictate the behavior and interactions of various compounds.