15. Chemical Kinetics
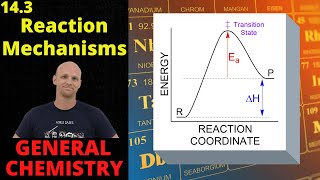
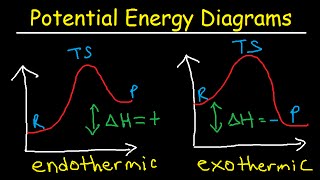
Energy Diagrams

Get help from an AI Tutor
Ask a question to get started.
Problem 122
Textbook Question
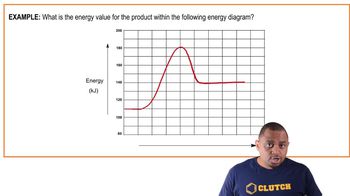
Textbook QuestionThe rates of many atmospheric reactions are accelerated by the absorption of light by one of the reactants. For example, consider the reaction between methane and chlorine to produce methyl chloride and hydrogen chloride: Reaction 1: CH41g2 + Cl21g2 ¡ CH3Cl1g2 + HCl1g2 This reaction is very slow in the absence of light. However, Cl21g2 can absorb light to form Cl atoms: Reaction 2: Cl21g2 + hv ¡ 2 Cl1g2 Once the Cl atoms are generated, they can catalyze the reaction of CH4 and Cl2, according to the following proposed mechanism: Reaction 3: CH41g2 + Cl1g2 ¡ CH31g2 + HCl1g2 Reaction 4: CH31g2 + Cl21g2 ¡ CH3Cl1g2 + Cl1g2 The enthalpy changes and activation energies for these two reactions are tabulated as follows: Reaction H 1kJ ,mol 2 Ea 1kJ ,mol 2 3 +4 17 4 -109 4 (b) By using the data tabulated here, sketch a quantitative energy profile for the catalyzed reaction represented by reactions 3 and 4.

 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
282
views
Was this helpful?
Related Videos
Related Practice
Showing 1 of 12 videos