Table of contents
- 1. Intro to General Chemistry3h 48m
- Classification of Matter18m
- Physical & Chemical Changes19m
- Chemical Properties7m
- Physical Properties5m
- Intensive vs. Extensive Properties13m
- Temperature12m
- Scientific Notation13m
- SI Units7m
- Metric Prefixes24m
- Significant Figures9m
- Significant Figures: Precision in Measurements8m
- Significant Figures: In Calculations14m
- Conversion Factors16m
- Dimensional Analysis17m
- Density12m
- Density of Geometric Objects19m
- Density of Non-Geometric Objects7m
- 2. Atoms & Elements4h 16m
- The Atom9m
- Subatomic Particles15m
- Isotopes17m
- Ions27m
- Atomic Mass28m
- Periodic Table: Classifications11m
- Periodic Table: Group Names8m
- Periodic Table: Representative Elements & Transition Metals7m
- Periodic Table: Element Symbols6m
- Periodic Table: Elemental Forms6m
- Periodic Table: Phases8m
- Periodic Table: Charges20m
- Calculating Molar Mass10m
- Mole Concept30m
- Law of Conservation of Mass5m
- Law of Definite Proportions10m
- Atomic Theory9m
- Law of Multiple Proportions3m
- Millikan Oil Drop Experiment7m
- Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment10m
- 3. Chemical Reactions4h 10m
- Empirical Formula18m
- Molecular Formula20m
- Combustion Analysis38m
- Combustion Apparatus15m
- Polyatomic Ions24m
- Naming Ionic Compounds11m
- Writing Ionic Compounds7m
- Naming Ionic Hydrates6m
- Naming Acids18m
- Naming Molecular Compounds6m
- Balancing Chemical Equations13m
- Stoichiometry16m
- Limiting Reagent17m
- Percent Yield19m
- Mass Percent4m
- Functional Groups in Chemistry11m
- 4. BONUS: Lab Techniques and Procedures1h 36m
- 5. BONUS: Mathematical Operations and Functions48m
- 6. Chemical Quantities & Aqueous Reactions3h 53m
- Solutions6m
- Molarity18m
- Osmolarity15m
- Dilutions15m
- Solubility Rules15m
- Electrolytes18m
- Molecular Equations18m
- Gas Evolution Equations13m
- Solution Stoichiometry14m
- Complete Ionic Equations18m
- Calculate Oxidation Numbers15m
- Redox Reactions17m
- Balancing Redox Reactions: Acidic Solutions17m
- Balancing Redox Reactions: Basic Solutions17m
- Activity Series10m
- 7. Gases3h 50m
- Pressure Units6m
- The Ideal Gas Law18m
- The Ideal Gas Law Derivations13m
- The Ideal Gas Law Applications6m
- Chemistry Gas Laws13m
- Chemistry Gas Laws: Combined Gas Law12m
- Mole Fraction of Gases6m
- Partial Pressure19m
- The Ideal Gas Law: Molar Mass13m
- The Ideal Gas Law: Density14m
- Gas Stoichiometry18m
- Standard Temperature and Pressure14m
- Effusion14m
- Root Mean Square Speed9m
- Kinetic Energy of Gases10m
- Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution8m
- Velocity Distributions4m
- Kinetic Molecular Theory14m
- Van der Waals Equation9m
- 8. Thermochemistry2h 37m
- Nature of Energy6m
- Kinetic & Potential Energy7m
- First Law of Thermodynamics7m
- Internal Energy8m
- Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions7m
- Heat Capacity19m
- Constant-Pressure Calorimetry24m
- Constant-Volume Calorimetry10m
- Thermal Equilibrium8m
- Thermochemical Equations12m
- Formation Equations9m
- Enthalpy of Formation12m
- Hess's Law23m
- 9. Quantum Mechanics2h 58m
- Wavelength and Frequency6m
- Speed of Light8m
- The Energy of Light13m
- Electromagnetic Spectrum10m
- Photoelectric Effect17m
- De Broglie Wavelength9m
- Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle17m
- Bohr Model14m
- Emission Spectrum5m
- Bohr Equation13m
- Introduction to Quantum Mechanics5m
- Quantum Numbers: Principal Quantum Number5m
- Quantum Numbers: Angular Momentum Quantum Number10m
- Quantum Numbers: Magnetic Quantum Number11m
- Quantum Numbers: Spin Quantum Number9m
- Quantum Numbers: Number of Electrons11m
- Quantum Numbers: Nodes6m
- 10. Periodic Properties of the Elements3h 9m
- The Electron Configuration22m
- The Electron Configuration: Condensed4m
- The Electron Configurations: Exceptions13m
- The Electron Configuration: Ions12m
- Paramagnetism and Diamagnetism8m
- The Electron Configuration: Quantum Numbers16m
- Valence Electrons of Elements12m
- Periodic Trend: Metallic Character3m
- Periodic Trend: Atomic Radius8m
- Periodic Trend: Ionic Radius13m
- Periodic Trend: Ionization Energy12m
- Periodic Trend: Successive Ionization Energies11m
- Periodic Trend: Electron Affinity10m
- Periodic Trend: Electronegativity5m
- Periodic Trend: Effective Nuclear Charge21m
- Periodic Trend: Cumulative12m
- 11. Bonding & Molecular Structure3h 29m
- Lewis Dot Symbols10m
- Chemical Bonds13m
- Dipole Moment11m
- Octet Rule10m
- Formal Charge9m
- Lewis Dot Structures: Neutral Compounds20m
- Lewis Dot Structures: Sigma & Pi Bonds14m
- Lewis Dot Structures: Ions15m
- Lewis Dot Structures: Exceptions14m
- Lewis Dot Structures: Acids15m
- Resonance Structures21m
- Average Bond Order4m
- Bond Energy15m
- Coulomb's Law6m
- Lattice Energy12m
- Born Haber Cycle14m
- 12. Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory1h 58m
- 13. Liquids, Solids & Intermolecular Forces2h 23m
- Molecular Polarity10m
- Intermolecular Forces20m
- Intermolecular Forces and Physical Properties11m
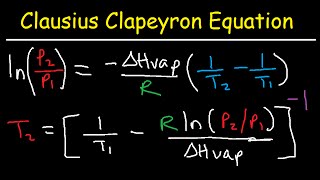
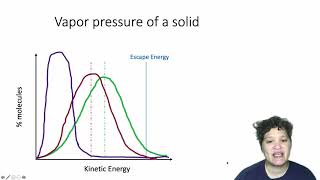
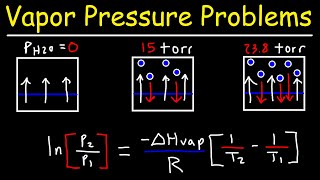
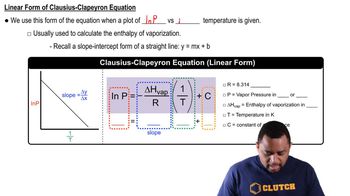
- Clausius-Clapeyron Equation18m
- Phase Diagrams13m
- Heating and Cooling Curves27m
- Atomic, Ionic, and Molecular Solids11m
- Crystalline Solids4m
- Simple Cubic Unit Cell7m
- Body Centered Cubic Unit Cell12m
- Face Centered Cubic Unit Cell6m
- 14. Solutions3h 1m
- Solutions: Solubility and Intermolecular Forces17m
- Molality15m
- Parts per Million (ppm)13m
- Mole Fraction of Solutions8m
- Solutions: Mass Percent12m
- Types of Aqueous Solutions8m
- Intro to Henry's Law4m
- Henry's Law Calculations12m
- The Colligative Properties14m
- Boiling Point Elevation16m
- Freezing Point Depression10m
- Osmosis19m
- Osmotic Pressure10m
- Vapor Pressure Lowering (Raoult's Law)16m
- 15. Chemical Kinetics2h 53m
- 16. Chemical Equilibrium2h 29m
- 17. Acid and Base Equilibrium5h 2m
- Acids Introduction9m
- Bases Introduction7m
- Binary Acids15m
- Oxyacids10m
- Bases14m
- Amphoteric Species5m
- Arrhenius Acids and Bases5m
- Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases21m
- Lewis Acids and Bases12m
- The pH Scale16m
- Auto-Ionization9m
- Ka and Kb16m
- pH of Strong Acids and Bases9m
- Ionic Salts17m
- pH of Weak Acids31m
- pH of Weak Bases32m
- Diprotic Acids and Bases8m
- Diprotic Acids and Bases Calculations30m
- Triprotic Acids and Bases9m
- Triprotic Acids and Bases Calculations17m
- 18. Aqueous Equilibrium4h 47m
- Intro to Buffers20m
- Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation19m
- Intro to Acid-Base Titration Curves13m
- Strong Titrate-Strong Titrant Curves9m
- Weak Titrate-Strong Titrant Curves15m
- Acid-Base Indicators8m
- Titrations: Weak Acid-Strong Base38m
- Titrations: Weak Base-Strong Acid41m
- Titrations: Strong Acid-Strong Base11m
- Titrations: Diprotic & Polyprotic Buffers32m
- Solubility Product Constant: Ksp17m
- Ksp: Common Ion Effect18m
- Precipitation: Ksp vs Q12m
- Selective Precipitation9m
- Complex Ions: Formation Constant18m
- 19. Chemical Thermodynamics1h 50m
- 20. Electrochemistry2h 42m
- 21. Nuclear Chemistry2h 37m
- Intro to Radioactivity10m
- Alpha Decay9m
- Beta Decay7m
- Gamma Emission7m
- Electron Capture & Positron Emission9m
- Neutron to Proton Ratio7m
- Band of Stability: Alpha Decay & Nuclear Fission10m
- Band of Stability: Beta Decay3m
- Band of Stability: Electron Capture & Positron Emission4m
- Band of Stability: Overview14m
- Measuring Radioactivity7m
- Rate of Radioactive Decay12m
- Radioactive Half-Life16m
- Mass Defect19m
- Nuclear Binding Energy14m
- 22. Organic Chemistry5h 7m
- Introduction to Organic Chemistry8m
- Structural Formula8m
- Condensed Formula10m
- Skeletal Formula6m
- Spatial Orientation of Bonds3m
- Intro to Hydrocarbons16m
- Isomers11m
- Chirality15m
- Functional Groups in Chemistry11m
- Naming Alkanes4m
- The Alkyl Groups9m
- Naming Alkanes with Substituents13m
- Naming Cyclic Alkanes6m
- Naming Other Substituents8m
- Naming Alcohols11m
- Naming Alkenes11m
- Naming Alkynes9m
- Naming Ketones5m
- Naming Aldehydes5m
- Naming Carboxylic Acids4m
- Naming Esters8m
- Naming Ethers5m
- Naming Amines5m
- Naming Benzene7m
- Alkane Reactions7m
- Intro to Addition Reactions4m
- Halogenation Reactions4m
- Hydrogenation Reactions3m
- Hydrohalogenation Reactions7m
- Alcohol Reactions: Substitution Reactions4m
- Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions9m
- Intro to Redox Reactions8m
- Alcohol Reactions: Oxidation Reactions7m
- Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions6m
- Ester Reactions: Esterification4m
- Ester Reactions: Saponification3m
- Carboxylic Acid Reactions4m
- Amine Reactions3m
- Amide Formation4m
- Benzene Reactions10m
- 23. Chemistry of the Nonmetals2h 39m
- Main Group Elements: Bonding Types4m
- Main Group Elements: Boiling & Melting Points7m
- Main Group Elements: Density11m
- Main Group Elements: Periodic Trends7m
- The Electron Configuration Review16m
- Periodic Table Charges Review20m
- Hydrogen Isotopes4m
- Hydrogen Compounds11m
- Production of Hydrogen8m
- Group 1A and 2A Reactions7m
- Boron Family Reactions7m
- Boron Family: Borane7m
- Borane Reactions7m
- Nitrogen Family Reactions12m
- Oxides, Peroxides, and Superoxides12m
- Oxide Reactions4m
- Peroxide and Superoxide Reactions6m
- Noble Gas Compounds3m
- 24. Transition Metals and Coordination Compounds3h 16m
- Atomic Radius & Density of Transition Metals11m
- Electron Configurations of Transition Metals7m
- Electron Configurations of Transition Metals: Exceptions11m
- Paramagnetism and Diamagnetism10m
- Ligands10m
- Complex Ions5m
- Coordination Complexes7m
- Classification of Ligands11m
- Coordination Numbers & Geometry9m
- Naming Coordination Compounds22m
- Writing Formulas of Coordination Compounds8m
- Isomerism in Coordination Complexes15m
- Orientations of D Orbitals4m
- Intro to Crystal Field Theory10m
- Crystal Field Theory: Octahedral Complexes5m
- Crystal Field Theory: Tetrahedral Complexes4m
- Crystal Field Theory: Square Planar Complexes4m
- Crystal Field Theory Summary8m
- Magnetic Properties of Complex Ions9m
- Strong-Field vs Weak-Field Ligands6m
- Magnetic Properties of Complex Ions: Octahedral Complexes11m
13. Liquids, Solids & Intermolecular Forces
Clausius-Clapeyron Equation
Struggling with General Chemistry?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first video
Clausius-Clapeyron Equation
Jules Bruno
Video duration:
59sPlay a video:
Related Videos
Related Practice