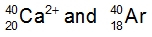Atoms are neutral entities characterized by an equal number of protons and electrons. However, when the balance between protons and electrons is disrupted, ions are formed. Ions arise from the loss or gain of electrons by an element. When an element loses electrons, it transforms into a positively charged ion known as a cation. This occurs because the loss of negatively charged electrons results in a net positive charge. Conversely, when an element gains electrons, it becomes a negatively charged ion called an anion, as the addition of negative electrons increases the overall negative charge.
It is essential to remember that cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions. A related concept is isoelectronic, which refers to different elements or ions that possess the same number of electrons. The key distinction between atoms and ions lies in their charge: atoms maintain an equal number of protons and electrons, while ions exhibit a difference in these quantities due to the gain or loss of electrons. Understanding this difference is crucial when studying the behavior and properties of ions in various chemical contexts.

 .
.