Textbook Question
Name the following:
c.
561
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: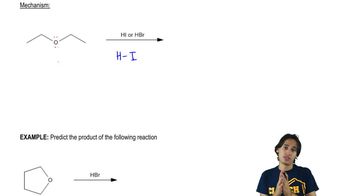



 1:32m
1:32mMaster How to name ethers using the common naming system. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning